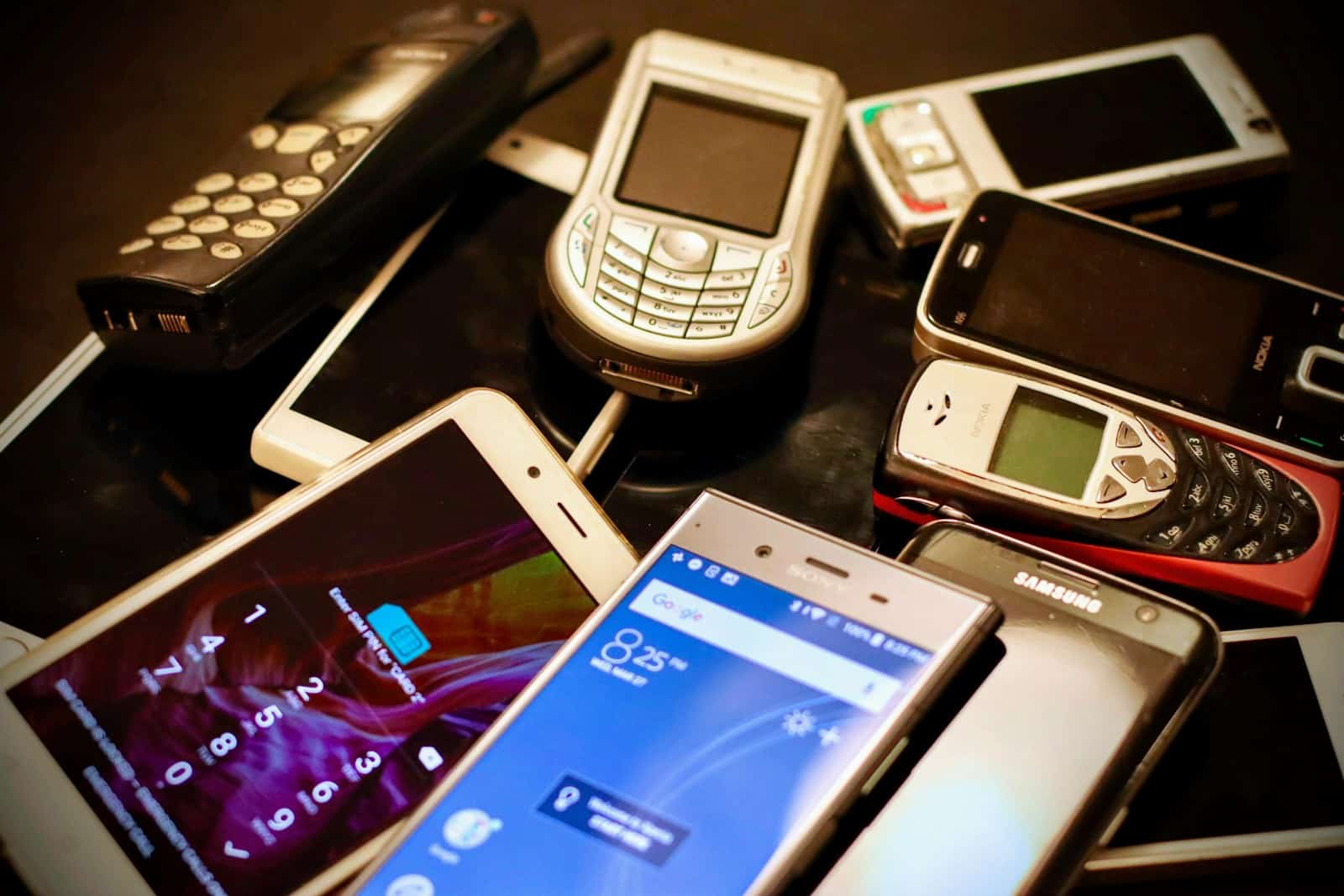
The history of cell phones has seen a significant evolution from the early days of mobile communication to its current state as an essential tool for billions of people worldwide. It all began in 1973 when Martin Cooper made the first mobile phone call, setting the stage for the technology that now allows people to connect without the constraints of wired telephones. Over the decades, there have been rapid technological advancements, transforming mobile phones from bulky and expensive devices to sleek and affordable handheld gadgets.
The continuous improvement of hardware and software has been central to this transformation, making phones more powerful and user-friendly. With each leap in technology, the functionality of mobile devices broadened, paving the way for the smartphones we rely on today. The influence of cell phones on society cannot be overstated. Once a luxury for the few, they have become a basic necessity, playing a central role in how people interact with each other and access information. Mobile phones reach across various aspects of modern life, influencing social behavior and driving new forms of communication and commerce.
The Past: Early Days

| Year | Event | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| 1973 | First Cell Phone Prototype | Motorola engineer Martin Cooper creates the first working prototype of a handheld cell phone. |
| 1983 | First Commercial Cell Phone | The Motorola DynaTAC 8000X, nicknamed “The Brick,” becomes the first commercially available cell phone. |
| 1991 | 2G Networks Launch | Introduction of 2G networks in Finland, improving call quality and enabling basic data transmission. |
| 1992 | First SMS Text Message | The first text message, reading “Merry Christmas,” is sent. |
| 1992 | IBM Simon | Considered the first ‘smartphone’, it had a touchscreen, email capability, and basic apps. |
| 1996 | Nokia 9000 Communicator | A clamshell design with a small internal screen and full keyboard, blurring the line between phone and PDA. |
| 1999 | BlackBerry 5810 | BlackBerry introduced push email to mobile devices, revolutionizing business communication. |
| 2000 | Camera Phones Introduced | The Sharp J-SH04 in Japan is considered the first mass-market camera phone. |
| 2007 | Apple iPhone Released | The iPhone’s touch-centric interface and focus on apps change the landscape of mobile phones forever. |
| 2008 | First Android Phone | The HTC Dream (T-Mobile G1) marks the debut of the Android operating system. |
Important Notes:
- This is simplified: There are countless other important innovations and devices that could be included, this is a highlight of major milestones.
- Subjectivity: What qualifies as a ‘smartphone’ is somewhat debatable in the early years.
The Present: Modern Technology
| Year | Event | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| 2008 | 3G Networks Widespread | Faster internet speeds on mobile devices enable web browsing and app functionality to truly flourish. |
| 2009 | App Store Launch | Apple’s App Store revolutionizes how users access and utilize mobile software. |
| 2010 | Rise of Social Media Apps | The popularity of social media apps like Facebook and Twitter explodes on smartphones. |
| 2011 | First Dual-Core Processors | Smartphones gain processing power, enabling more demanding games and applications. |
| 2011 | 4G Networks Emerge | 4G networks offer even faster data speeds, further transforming mobile browsing and streaming. |
| 2013 | Fingerprint Scanners | Fingerprint scanners become mainstream, enhancing phone security. |
| 2014 | Large-Screen Phones Popularize | Phablets (large-screen phones) like the Samsung Galaxy Note series gain popularity. |
| 2016 | Bezel-Less Displays | Phones with minimal bezels surrounding the screen become a design trend. |
| 2017 | Artificial Intelligence Integration | AI assistants like Siri and Google Assistant become commonplace in smartphones. |
| 2019 | 5G Networks Deployed | 5G promises significantly faster data speeds and lower latency, ushering in new mobile experiences. |
| 2020-Present | Foldable Phones | Foldable smartphones with flexible displays emerge as a new design direction (still evolving). |
The Future: Looking Forward

| Year | Event (Predicted) | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| 2020-2024 | Increased Focus on Foldables | Foldable phone technology improves in durability, affordability, and functionality, becoming a more mainstream option. |
| 2021-2025 | Advancements in Under-Display Tech | Fingerprint scanners and potentially even front-facing cameras become integrated seamlessly under the display. |
| 2023-2027 | Widespread 5G Adoption | 5G networks become more widely available, offering significant improvements in download and upload speeds for mobile data users. |
| 2024-2028 | Enhanced AR/VR Integration | Smartphones become more powerful and integrated with AR/VR experiences, potentially blurring the lines between physical and digital worlds. |
| 2025+ | Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) Integration (Speculative) | Highly speculative: Brain-computer interfaces could allow for intuitive phone control through thought alone. |
| 2020+ | Continued Focus on Biometric Security | Facial recognition, iris scanners, and other biometric security features become more sophisticated and widely used. |
| 2020+ | Increased Focus on Sustainability | Manufacturers prioritize eco-friendly materials and longer lifespans for phones to reduce e-waste. |
Important Notes:
- Predictions are not guaranteed: These are predictions based on current trends and may not come to fruition exactly as described.
- BCI Integration highly speculative: Brain-computer interface integration is a highly speculative development with many technological and ethical hurdles.
Key Takeaways
- Mobile phones have evolved from Martin Cooper’s first call in 1973 to essential everyday devices.
- Technological improvements have made phones more powerful and accessible to a wider audience.
- Cell phones have significantly influenced communication and society as a whole.
The Birth of the Cell Phone
The cell phone revolution began with a groundbreaking invention that led to the mobile devices we rely on today. This journey from concept to everyday essential started in the early 1970s and forever changed how we communicate.
The Genesis of Mobile Phones
Mobile communication traces back to the early two-way radios, initially used by police departments and in the military. In the 1940s, this technology evolved into something more personal. Bell Labs played an instrumental role in laying the groundwork for mobile telephony, even before the first true handheld cell phone came into existence. Their efforts set the foundation of cellular networks that would allow multiple users to make calls within a defined area known as a “cell”.
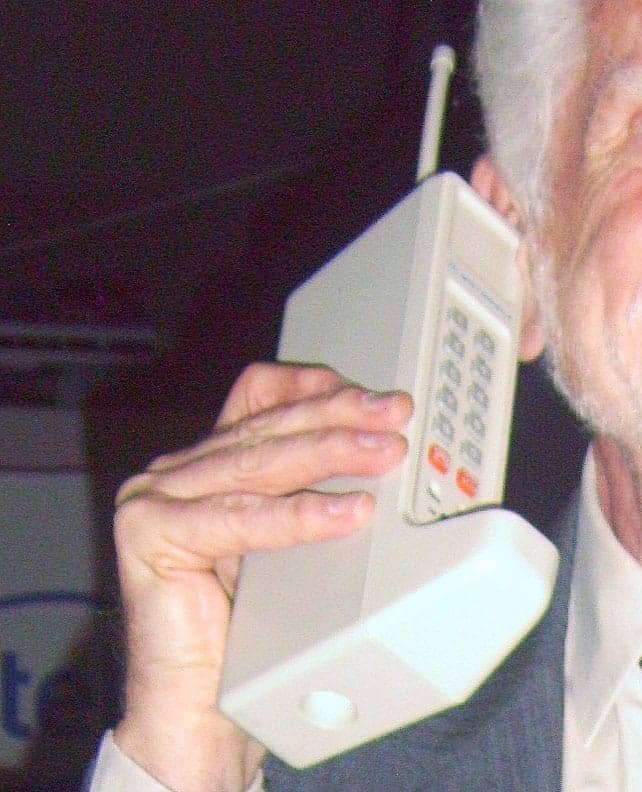
On June 17, 1946, AT&T introduced the Mobile Telephone Service (MTS) in St. Louis, Missouri, though it was limited to major cities and was mostly installed in vehicles due to its size. This service was a stepping stone towards personal communication, but it wasn’t until April 3, 1973, that Martin Cooper, an engineer at Motorola, made the first call on a truly portable cellular phone.
Invention and Early Development
In the 1970s, Martin Cooper, an engineer at Motorola, led the charge in creating the world’s first handheld mobile phone. His vision centered on making communication possible without the constraints of fixed locations. This idea took shape when he and his team developed a prototype that would allow calls to be made while on the move. The formative years of mobile telephony were marked by significant research and development challenges, but the determination of these pioneers lay the groundwork for the mobile revolution.
Cellphone History: From Bricks to Smartphones
| Period | Technology | Key Features | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1908 – 1940s | Early Mobile Telephony | – Radio telephones in cars and other vehicles – Large, heavy devices – Limited range and coverage | – Paved the way for future development – Used primarily by professionals |
| 1946 – 1973 | Car Phones and Early Mobile Networks | – First commercial car phone networks in Chicago (1946) – Mobile phone systems like NMT in Europe (1969) – Still large and expensive | – Increased accessibility and usage – Primarily owned by businesses and wealthy individuals |
| 1973 – 1983 | First Generation (1G) Cellular Networks | – Motorola DynaTAC 8000X (1983): first commercially available handheld phone – Analog signal technology – Limited capacity and battery life | – Introduction of portable, personal mobile phones – Still a niche product due to high cost |
| 1983 – 1992 | Second Generation (2G) Cellular Networks | – Improved digital signal technology – Increased capacity and call quality – Introduction of features like caller ID and text messaging | – Widespread adoption of mobile phones – Used for communication and basic information access |
| 1992 – 2007 | Third Generation (3G) Cellular Networks | – Introduction of internet capabilities – Faster data speeds, enabling mobile browsing and email – Development of multimedia features like video calling and camera phones | – Mobile phones become indispensable for communication, information, and entertainment – Rise of mobile applications and the “app store” concept |
| 2007 – Present | Fourth Generation (4G) and Beyond | – High-speed internet access, comparable to home broadband – Enables video streaming, music downloads, and real-time communication – Smartphones with large touchscreens and advanced operating systems | – Mobile phones transform into pocket computers – Essential tool for work, social interaction, and daily life |
Additional Notes:
- This table provides a simplified overview of cellphone history. Each period saw various technological advancements and milestones.
- The transition from bulky, voice-only devices to pocket-sized, multi-functional smartphones has revolutionized communication, information access, and entertainment.
- Cellphone technology continues to evolve, with 5G networks and emerging technologies promising even faster speeds and greater connectivity.
The DynaTAC Era and Beyond
Motorola introduced the DynaTAC 8000X in the early 1980s after more than a decade of development. This device was a far cry from today’s sleek smartphones. It was large, weighing almost two pounds, and had a limited call duration of just half an hour. Despite these limitations, the Motorola DynaTAC 8000X was a marvel of its time, offering untethered communication to those who could afford its hefty price tag. It marked the beginning of a new era in personal communication, paving the way for the dynamic and diverse range of cell phones that would follow.
A Look At The DynaTAC
| Feature | Detail |
|---|---|
| Weight | 2.4 lb (1.1 kg) |
| Dimensions | 9.1 x 5.1 x 1.8 in |
| Talk time | 30 minutes |
| Recharge time | 10 hours |
Technological Advancements in Mobile Phones
Mobile phones have come a long way since their inception, transforming from simple communication tools to multifaceted, high-tech devices. This section traces the evolution of mobile technologies, from network capabilities and design changes to hardware innovations that have revolutionized how we use our phones today.
From 1G to 5G: A Wireless Journey
This first generation of cellular technology, known as 1G, was just the beginning; engineers continued to refine antennas and radio transceivers to enhance the user experience. Innovations allowed the expansion of coverage areas, increased call quality, and eventually, the miniaturization of the cell phone components. These advancements led to a range of iconic handsets in the following decades, like the sleek Motorola Razr and the technically advanced Mobira Cityman 900, each playing their part in driving the evolution of cell phone history forward.
Each new generation, from 2G to the current 5G, brought improvements in speed and connectivity. 3G introduced faster data transmission, enabling web browsing and email on phones. 4G further increased speeds, allowing for high-definition video streaming and enhanced gaming experiences. Today, 5G is rolling out globally, promising unprecedented speed and the capacity to connect more devices simultaneously.
Analog to Digital Transition
The first generation of mobile phones, known as 1G, began with analog technology. Clear voice calls were a significant upgrade from the prior reliance on landlines. They used frequencies that could only handle voice calls, without any encryption, which meant calls were not secure.
The Advent of 2G and SMS
With the switch to 2G networks, mobile phones leaped from analog to digital. The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) was a key player in this era. In the early 1990s, digital encryption made calls more secure. Plus, 2G introduced us to SMS (Short Message Service), changing how we text by allowing messages of 160 characters.
3G’s Impact on Connectivity
3G networks came around in the 2000s, boosting speed and opening the door for mobile phones to connect to the internet. Web browsing, email checking, and video streaming on-the-go became realities. The user experience on cell phones became richer and more interactive.
4G and Mobile Internet
Then 4G, with its Long-Term Evolution (LTE) protocols, stepped up the game with even higher internet speeds. It set the stage for HD video streaming, high-quality video calls, and robust mobile gaming experiences. Data could now travel at unprecedented speeds, letting us share and receive information in a flash.
5G and The Future
The advent of 5G was a remarkable advancement in mobile network technology. It boasts incredibly fast speeds, providing almost instant downloads and seamless high-definition streaming. 5G’s ultra-low latency is paramount for real-time applications such as remote surgery and self-driving vehicles. Additionally, its capability to handle enormous numbers of connected devices will accelerate the growth of the Internet of Things. With the help of features like network slicing, 5G can optimize itself for specific requirements. 5G is a revolutionary technology with the potential to transform industries and fundamentally alter how we interact with the world.
Here’s a table comparing the different generations of cellular technology:
| Feature | 1G | 2G | 3G | 4G | 5G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Launch Period | 1980s | Early 1990s | Early 2000s | ~2010 | 2019+ |
| Technology | Analog | Digital (GSM, CDMA) | Enhanced Digital (UMTS, CDMA2000) | LTE, WiMAX | New Radio (NR) |
| Key Improvements | Basic voice calls | Voice + text messaging, limited data | Faster data speeds, mobile internet | Much faster speeds, video streaming, low latency | Massive speed increase, very low latency, supports many more devices |
| Typical Max Speed | N/A | ~14.4 Kbps to 64 Kbps | ~2 Mbps | ~100 Mbps | 1- 10 Gbps+ |
| Latency (delay) | High | Medium | Lower | Low | Extremely Low |
Additional Notes:
- Speeds are theoretical maximums: Real-world speeds will vary based on network conditions, location, and device capabilities.
- 5G is still evolving: 5G technology is still being rolled out and improved, so its full potential is yet to be realized.
- Overlap between generations: Newer generations don’t immediately replace older ones. Networks often maintain multiple technologies for compatibility.
The Smartphone Revolution
Smartphones have become pivotal in the cell phone evolution. Early models replaced the traditional keyboards with touchscreens, making way for more intuitive user interfaces. The introduction of smartphones by companies like Nokia paved the way for future innovations. Today, powerhouses like Samsung continue to push the envelope, developing sleek designs and advanced features that define modern communication.
The Introduction of Smartphones
The evolution of mobile phones took a game-changing turn with the introduction of the IBM Simon in 1992. It was the first device to combine features like a touchscreen, email, and fax capabilities, setting the stage for modern smartphones. By mid-1994, this gadget hit the market, laying down the groundwork for the devices we rely on today. During the late 1990s, other key players, such as Nokia, began to experiment with this format, producing models like the Nokia 9000 Communicator. This device integrated features like a QWERTY keyboard, making it a forerunner for future business-centric phones.
In 2000, the launch of Japan’s DoCoMo i-mode gave rise to the concept of mobile internet services, while the first camera phone, the SCP-5300, introduced by J-Phone in Japan in the same year, began to redefine the mobile phone as more than just a communication device.
The Era of iPhone and Android
The year 2007 was a watershed moment with the introduction of the Apple iPhone. The iPhone revolutionized the smartphone concept with its sleek design, user-friendly touchscreen, and a remarkable new feature—the App Store. Apple’s iOS turned into a major platform for mobile applications, transforming the iPhone into a portable computer that could fit in your pocket.
Shortly after the iPhone’s release, the first phone using the Android operating system was launched, signaling the beginning of a new competitor in the smartphone market. This open-source platform enabled companies like Samsung and HTC to offer their own smartphones, leading to a diverse and innovative environment that pushed smartphone technology forward at a rapid pace. Variety in software and hardware accelerated the adoption of smartphones, making them a dominant force. They moved from luxury items to essential tools for everyday life, supported by ever-expanding cellular networks.
Smartphones have grown to replace numerous devices, integrating cameras, gaming consoles, and personal computers all into one handheld device. With leading brands like Apple and Samsung, alongside significant contributions from companies like BlackBerry and Nokia, this technology continues to expand, bringing new functionalities with each release.
Key Innovations in Hardware
Early mobile phones were bulky with limited functionality, but over time, hardware components such as batteries, cameras, and screens have transformed dramatically. The Apple iPhone and Samsung smartphones have pioneered advancements with their lighter, stronger batteries, which now last much longer. Cameras on mobile phones have evolved from simple image capturing tools to sophisticated systems capable of professional-quality photography and videos.
As mobile phones transformed into smartphones, their hardware also underwent significant upgrades. Early camera phones had low-quality images, but today, smartphones boast cameras that rival professional equipment. Devices like the Razr reinvented the flip phone with a slim profile and advanced features. Meanwhile, evolving storage capacities and processors have turned smartphones into portable computers, capable of a wide range of functions beyond their original intent for calls and texts.
- Displays: High-resolution screens with vivid colors are now standard.
- Touchscreens: The evolution from physical buttons to intuitive touchscreens.
Modern smartphones incorporate sensors that register gestures and touches with great precision.
Software and Operation System Evolution
Software and operating systems have evolved in tandem with hardware improvements to offer a more dynamic experience. The development of mobile operating systems like iOS for the iPhone and Android for a multitude of devices has made smartphones incredibly powerful and user-friendly. Encrypted communication ensures that text messaging and wireless communication remain secure from unauthorized access.
- Bluetooth enables wire-free, short-range communication between devices.
- AI and ML: Cutting-edge algorithms power features like predictive text and voice assistants.
From the earliest Motorola models to today’s high-end smartphones, both software and hardware advancements continue to shape the field of mobile electronics.
The Rise of Mobile Software and Services
This section explores the pivotal shift in mobile technology brought about by innovative software and essential services. It delves into the creation and development of operating systems like Android and iOS, the burgeoning app ecosystem, and advancements in mobile internet and connectivity.
Operating Systems: Android and iOS
Android was introduced in 2008, and Google backed it as an open-source platform, encouraging widespread adoption by various phone manufacturers. On the other hand, iOS, launched with the first iPhone in 2007, is Apple’s proprietary operating system, offering a seamless experience across Apple devices.
- Android: Powering brands like Samsung, HTC, and Motorola.
- iOS: Exclusive to Apple’s iPhone, iPad, and iPod Touch.
Both systems support a vast range of apps and services, with regular updates enhancing security, functionality, and user interface.
The App Ecosystem
The App Store and Google Play serve as the central hubs for downloading a myriad of apps, both free and paid. The introduction of the App Store in 2008 signified a major leap, setting the stage for app developers to innovate and capture the market.
- Games, social media, and utility apps have become integral to daily life.
- Text messaging has evolved through apps providing SMS and internet-based messaging services.
The availability of these apps has shaped how people communicate, work, and entertain themselves on their mobile devices.
Mobile Internet and Connectivity Features
Mobile internet access has transformed phones into essential tools for real-time information. 3G, 4G, and now 5G networks have progressively allowed faster and more reliable internet connections.
- Early phones offered basic services like text messages.
- Modern smartphones feature advanced connectivity, including WiFi, Bluetooth, and GPS.
Siri, Apple’s virtual assistant, debuted on the iPhone 4S in 2011, enhancing user interaction with both the device and the internet through voice-activated commands. Many apps and services rely on internet connectivity to function, further cementing the importance of robust mobile internet services.
This remarkable progress in mobile software and services continues to expand the capabilities of smartphones and fundamentally change how people interact with technology and each other.
Societal Impact of Cell Phones
Cell phones have significantly altered the fabric of society. They’ve reshaped how people interact and integrate technology into their daily lives. With the advent of smartphones, this impact only deepened, influencing communication norms, personal habits, and expectations for the future.
Changing Patterns of Communication
Cell phones have introduced new ways for individuals to communicate. They’ve moved beyond voice calls to text messages, emails, and various forms of instant messaging. This shift has made it possible for people to stay in constant contact. The ease of reaching out to anyone at any time has contributed to the expectation of immediate responses.
- Before Cell Phones: Face-to-face meetings and landline calls were the norms.
- After Cell Phones: Texting, social media, and video calls grew in popularity.
Cell Phones in Personal and Work Life
The line between personal and professional use of mobile phones has blurred. In the professional sphere, these devices have become tools for productivity. They facilitate remote work with functions like email access and cloud-based apps.
In personal lives, smartphones serve as a hub for managing tasks and social connections.
- Personal Use: Planning events, managing finances, or ordering food.
- Work Use: Responding to work emails, participating in virtual meetings, and accessing shared documents.
Future Trends and Potential
The future of mobile phones points toward further integration with daily life. Innovations promise advancements in areas like wireless communication and personal networking. Researchers are examining ways to leverage mobile technology to solve complex problems in science and healthcare.
- Innovation: New technology may lead to phones with longer battery life or better integration with other smart devices.
- Science and Healthcare: Mobile phones can play a role in telemedicine and real-time health monitoring.
Cell phones have become indispensable in society, impacting how we communicate, manage our lives, and look toward the future.
Design and User Interface Innovations
Cell phone technology has surged forward with significant changes in design and user interfaces, dramatically altering how we interact with our devices.
Transition from Keyboards to Touchscreens
In the early stages of cell phone evolution, devices featured physical keyboards that were anything but subtle. The keys stuck out, and the phones were quite bulky. A revolutionary shift came with the introduction of touchscreens. The first widely recognized touchscreen phone, the iPhone, was introduced by Apple in 2007.
This move towards touchscreens represented a leap towards simplicity in design and efficiency in user interface. Smartphones now could discard the physical buttons, freeing up space for a larger display and enabling a multitude of functions with just a simple touch. The Sharp J-SHO4, released in 2000, was a forerunner in this transition, being the first to include a built-in camera and color screen in a mainstream device.
Touchscreens also opened up the opportunity for a more personal and direct interaction. Users could now tap, swipe, and pinch, substantially easing navigation and control. The design of smartphones moved to sleek and minimalist, reflecting the demand for an interface that was more intuitive and user-friendly.
Impact of Mobile Phones on Society
As mobile phones have become ubiquitous, their influence has radically transformed how individuals interact and manage their daily activities.
Changes in Communication Practices
Mobile phones have revolutionized communication by making it possible to connect with anyone at almost any time. In the past few decades, the evolution from basic cell phones to advanced smartphones has been significant. Initially, a mobile phone’s primary function was to make voice calls. Nowadays, text messaging serves as a cornerstone for everyday interaction, especially among younger generations. Services such as SMS (Short Message Service) and later, instant messaging apps, have prompted a shift from voice calls to text-based exchanges. This shift has introduced new norms and etiquettes around communication, with people favoring quick, concise text exchanges over more time-consuming phone calls.

Influence on Daily Life and Convenience
The impact of mobile phones extends well beyond communication. Smartphones, equipped with powerful processors and advanced features, have become pocket-sized computers. They cater to a wide range of needs and tasks, from navigation and shopping to entertainment and healthcare. Smartphones have also spurred advancements in sectors like mobile banking, allowing users to manage their finances with a few taps on their screen. This level of convenience was unimaginable a few decades ago. In the United States, for instance, people rely on their smartphones for daily tasks, such as ordering transportation, finding restaurants, or scheduling appointments, signifying a profound adjustment in lifestyle and societal operations. Mobile technology has, therefore, become an integral part of life, with its absence almost unthinkable in many societies today.
Mobile Phone Security and Privacy
As mobile phones have become vital in our daily lives, the importance of safeguarding our personal information on these devices has intensified. Our discussions, personal notes, and private photos, among other things, demand strong security measures to keep them safe from prying eyes.
Encryption and Data Protection
Encryption is a technology that scrambles data so only authorized people can understand it. This is the foundation of data protection on mobile phones. When you encrypt your phone, all your images, texts, and sensitive info turn into unreadable code to anyone without your password. This way, even if someone gets your device, your privacy stays protected.
Mobile phones have adopted various encryption strategies over the years to enhance safety and confidentiality. For instance, smartphones now typically encrypt all the data stored on them by default. This means that your private conversations, payment details, and work emails are shielded from potential intruders.
Technology has also advanced to use sophisticated passwords and bio-metrics like fingerprint scanners to lock devices. Strong passwords are crucial because they act as the first line of defense against unauthorized access, keeping your information confidential. Both Apple and Android have developed systems that keep your data secure even if their servers are compromised.
Industry and Market Evolution
The cell phone industry has witnessed dramatic changes with various key players shaping the competitive landscape over the decades.
Major Players and Competitive Landscape
Initially, companies like Motorola and Nokia dominated the market. Motorola made headlines with their iconic StarTAC, the first clamshell (flip) phone, while Nokia captured customers’ favor with durable phones and the classic game, Snake. These were the industry giants in the early days of mobile phones.
As technology progressed, the entrance of the iPhone by Apple marked a pivotal shift, redefining the concept of smartphones. With a touch screen and an appealing user interface, the iPhone attracted a massive customer base, making Apple a dominant force in the industry. Competition intensified as companies like Samsung emerged as major players, introducing Android-powered smartphones that offered various features and became popular among a broad customer base.
Post-2010, the marketplace for cell phones further evolved with companies intensely competing on technological advancements, customer-centric features, and global market penetration. BlackBerry, once revered for prioritizing business communication with its physical keyboard, struggled to maintain its influence in the face of smartphones’ touch screen revolution.
Japanese company NTT DoCoMo has also been pivotal, especially in the field of pioneering early Internet connectivity with i-mode, setting standards for mobile internet services that preceded the smartphone era.
Today, Samsung and Apple remain titans in the smartphone space, with a significant share of the market captured by these two. Their reputations as innovators continue to set them apart as they evolve in response to emerging technologies and consumer demands. The industry continues to be customer-driven, with companies persistently advancing to meet and exceed expectations.
Future Outlook of Cellphone Technology
As technology races forward, the cellphone industry prepares for a new wave of innovations that promise to redefine communication and personal tech.
Potential Developments and Innovations
Connectivity: The spread of 5G technology will continue, offering faster speeds and more reliable connections. Innovations in antennas and network infrastructure are expected to enable this leap forward, with companies like Samsung and Motorola at the forefront of 5G-enabled devices.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Smartphones will likely harness AI and ML more effectively to provide personalized experiences. Future smartphones might predict user needs and automate tasks, from sorting photos to managing schedules. The integration of AI could also improve battery life and optimize device performance.
- AI in Photography: Smartphones will use advanced ML algorithms to enhance image quality, offering professional-grade photos.
- AI for Health: With AI, future smartphones might monitor health vitals, providing users with timely healthcare data.
Hardware Innovations: Foldable phones may become more commonplace, offering larger screens that can be conveniently tucked away. Companies such as Samsung are already releasing foldable models, indicating a trend that’s set to grow.
Sustainability: As consumers become more environmentally conscious, smartphone manufacturers like Nokia are focusing on sustainable practices. Future devices might feature recycled materials and be designed with longer lifespans in mind.
- Biodegradable Components: Innovations may include parts that are easier to recycle or that decompose over time.
- Energy Efficiency: Handset makers will likely prioritize energy-saving features to extend battery life and reduce environmental impact.
User Experience: The future of smartphones will not just be about hardware. Software and the overall user experience will see significant improvements. Anticipate intuitive interfaces and seamless integration with a range of smart devices, as companies strive to create a more interconnected and user-friendly ecosystem.
In summary, cellphone technology is expected to evolve with a strong emphasis on 5G, AI, sustainable innovation, and enhanced user experiences. Led by giants like Apple, Samsung, and Nokia, the next generation of smartphones will embody these advancements, as they continue to play a pivotal role in everyday life.
Frequently Asked Questions
These are common questions people have about the history of mobile phones and their development over the years.
Who is credited with inventing the first mobile phone?
Martin Cooper, a former vice president at Motorola, is often recognized as the inventor of the first practical mobile phone. He made the first cellular phone call in 1973.
When was the first mobile phone released to the public?
The first mobile phone available to the public was the Motorola DynaTAC 8000X, released in 1983. It was large and expensive by today’s standards.
How has mobile phone technology evolved since its inception?
Mobile phone technology has evolved from basic voice communication devices to multifunctional smartphone platforms. These devices now feature advanced computing capabilities, internet connectivity, high-resolution touch screens, and access to countless apps.
What year did mobile phones gain mass market popularity?
Mobile phones became widely popular in the late 1990s and early 2000s. This was due to the availability of more affordable and compact handsets as well as the introduction of digital networks that improved coverage and call quality.
How did mobile phones function in the early years of their existence?
In the early days, mobile phones were primarily designed for making and receiving voice calls. Text message functionality was later added, and early mobile phones had limited battery life and no internet connectivity.
What were the key technological advancements in mobile phone history between 1973 and 2017?
Key advancements from 1973 to 2017 include the transition from analog to digital networks, the introduction of text messaging and mobile internet, the evolution from basic handsets to smartphones, the development of touch screen technology, and the expansion of app ecosystems that transformed mobile phones into versatile personal devices.