Magnetometer screening is essential for maintaining security and safety in many places. Unlike traditional metal detectors, magnetometers measure the strength of a magnetic field to detect hidden metal objects. They help ensure that dangerous items do not enter buildings or events, improving overall security.
Both new and traditional magnetic screening methods are crucial for identifying threats. Walk-through magnetometers and handheld detectors are widely used in airports, schools, and public events. These devices help professionals find metallic objects quickly and efficiently.
Evolv Express® is a newer technology that combines sensors and artificial intelligence to identify weapons while ignoring harmless items. This innovation enhances security checks, making them smoother and respecting personal privacy. Many organizations now adopt these advanced systems to improve their security measures.
Image Credit: user:seleonov, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Magnetometer Screening: Unveiling Security’s Hidden Guardian
Magnetometer screening, a cornerstone of modern security protocols, utilizes the principles of magnetism to detect metallic objects. This technology is widely employed in various settings, from airports and government buildings to schools and event venues, to ensure the safety and security of individuals and premises.
How Does Magnetometer Screening Work?
Magnetometers operate by generating a magnetic field and monitoring any disturbances caused by the presence of ferromagnetic materials, such as iron and steel. When a person carrying a metallic object passes through the magnetometer’s detection zone, the object disrupts the magnetic field, triggering an alarm.
Types of Magnetometer Screening Systems
There are two primary types of magnetometer screening systems:
- Walk-Through Metal Detectors (WTMDs): These are the familiar archway-like devices commonly found in airports and other high-security areas. They utilize pulsed induction technology to detect metal objects concealed on or within a person’s body.
- Handheld Metal Detectors (HHMDs): These portable devices are used for more targeted searches, such as scanning individual bags or patting down individuals. They are often used in conjunction with WTMDs to pinpoint the location of detected metal objects.
Applications of Magnetometer Screening
Magnetometer screening finds application in a wide range of security contexts:
- Aviation Security: WTMDs are a standard feature in airport security checkpoints to detect weapons, explosives, and other prohibited items.
- Government Buildings: Magnetometer screening is employed in government buildings to prevent unauthorized entry of weapons and other potentially dangerous objects.
- Schools: Some schools have adopted magnetometer screening to deter students from bringing weapons onto campus and create a safer learning environment.
- Event Venues: Magnetometer screening is increasingly used at concerts, sporting events, and other large gatherings to ensure the safety of attendees.
- Correctional Facilities: Magnetometers are used in prisons and jails to prevent the smuggling of contraband items.
Image Credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/35838730@N05/14489505482
The Effectiveness of Magnetometer Screening
Magnetometer screening is a highly effective tool for detecting metallic weapons and other prohibited items. However, it is not foolproof, as it cannot detect non-metallic weapons or explosives. Therefore, it is often used in conjunction with other security measures, such as X-ray scanners and physical searches, to provide a comprehensive security solution.
The Future of Magnetometer Screening
As technology continues to advance, magnetometer screening is expected to become even more sophisticated and effective. Researchers are developing new types of magnetometers that can detect a wider range of materials, including non-metallic weapons and explosives. Additionally, artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are being integrated into magnetometer screening systems to improve their accuracy and efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Magnetometer screening measures magnetic fields to find hidden metal objects.
- Modern systems use sensors and AI to improve detection and privacy.
- Effective screening tools are vital for securing public spaces.
Fundamentals of Magnetometer Screening
Magnetometer screening helps detect metal objects in various settings. It utilizes different types of magnetometers and principles of metal detection to identify both ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Understanding Magnetometers
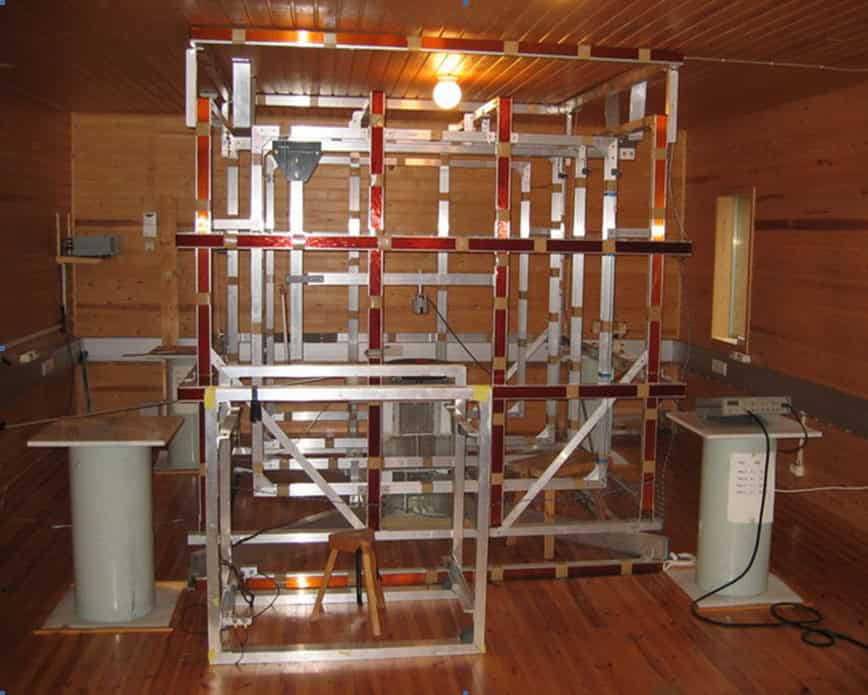
Magnetometers measure magnetic fields. They come in many kinds, with each type using different methods to measure magnetic strength and make it possible to detect metal objects. Some common types include fluxgate magnetometers, SQUID magnetometers, and anisotropic magnetoresistive (AMR) sensors.
Magnetometers can be sensitive and accurate, detecting small changes in magnetic fields caused by nearby metal objects. They help in finding buried items, like steel tanks or archaeological features, by sensing magnetic field anomalies.
Types of Magnetometers
Fluxgate magnetometers are popular for their stability and sensitivity. They use a core of magnetic material to detect changes in magnetic fields.
SQUID magnetometers are highly sensitive and can measure very weak magnetic fields. They use superconducting loops to detect changes.
AMR sensors use changes in resistance caused by magnetoresistive effects to detect magnetic fields. These sensors are useful in many applications due to their compact size and efficiency.
Different types of magnetometers have varied uses, from industrial applications to security screening.
Metal Detection Principles
Metal detectors use principles of magnetism and electricity to find metal objects. They typically send an electromagnetic field into the ground and measure the response from any metal object.
Ferrous metals, like iron, react strongly due to their magnetic properties. Non-ferrous metals, such as aluminum, also cause a detectable response but have different magnetic reactions.
Detection zones are areas where a metal object can be detected. These zones rely on the strength and distribution of the magnetic field. Accuracy in these zones varies depending on the type of detector used and the environment.
By understanding these principles, magnetometer screening effectively finds metal objects, enhancing security and safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
Magnetometers and metal detectors play essential roles in security. Yet, there are differences between them. This section addresses their unique functions, applications in airports, and the role of advanced technology in enhancing security.
How do magnetometers differ from metal detectors in security screening?
Magnetometers measure magnetic fields to detect metal. Metal detectors, on the other hand, use electromagnetic fields. Both identify objects, but magnetometers excel in detecting changes in magnetic fields, making them suitable for detailed screenings.
What are the primary uses of magnetometers in airport security?
In airports, magnetometers are vital for detecting hidden metal objects. They screen passengers and luggage for weapons or prohibited items. Their sensitivity helps identify smaller metal objects that might go unnoticed with other tools.
How does Advanced Imaging Technology enhance airport security screening?
Advanced Imaging Technology (AIT) uses millimeter waves to produce detailed images of passengers. This technology can highlight concealed items, ensuring a high level of security. AIT complements magnetometers by providing a clear image of potential threats without physical contact.
For what purposes are magnetometer screenings conducted at airports?
Magnetometer screenings at airports aim to detect hidden metal items. This includes weapons, contraband, and other illegal objects. By doing so, airports enhance passenger safety and comply with international security standards.
Are magnetometers standard in all modern mobile phones?
Yes, most modern mobile phones have built-in magnetometers. These sensors help with navigation and orientation by detecting magnetic fields. Although their primary use in phones is for navigation, they also aid in various applications like metal detection apps.
What technological principles enable magnetometers to detect metal objects?
Magnetometers work by measuring magnetic fields. When a metal object disrupts this field, the magnetometer detects the change. This principle allows them to identify both ferrous and non-ferrous metals, making them effective in various security applications.