16:9 resolutions are key in modern video and display tech. They set the standard for most TVs, computer screens, and online videos we see today. The most common 16:9 resolutions are 720p (1280×720), 1080p (1920×1080), 1440p (2560×1440), and 4K (3840×2160). Understanding aspect ratios and resolutions can help you make informed decisions about your display choices. Whether you’re buying a new TV, monitor, or smartphone, consider the 16:9 aspect ratio and the resolution that best suits your needs.
This widescreen aspect ratio gives a wider view than older 4:3 screens. It fits more on screen and looks more like what our eyes see. 16:9 is now used for most new content, from movies to YouTube videos.
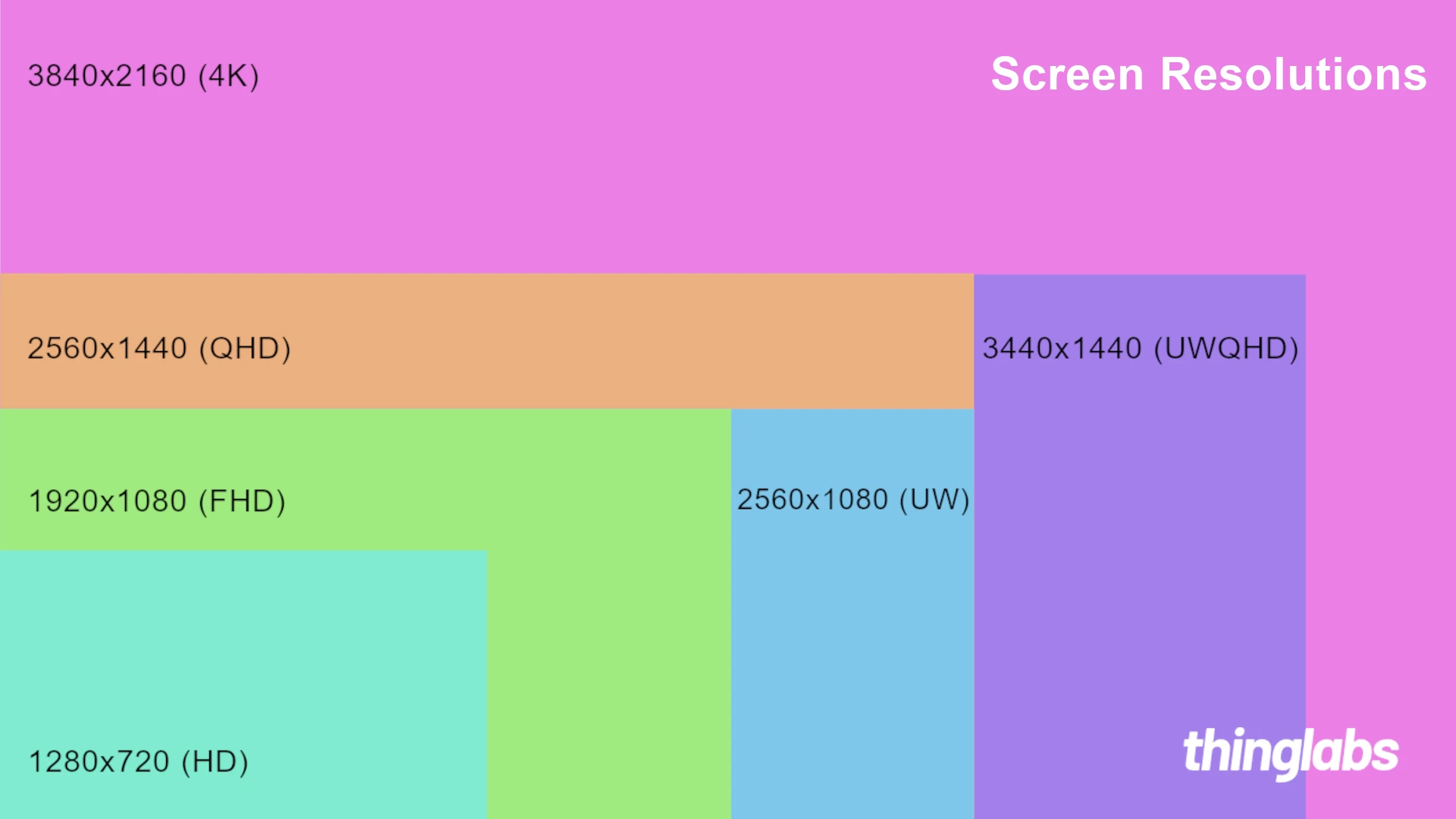
Picking the right 16:9 resolution matters for clear images and smooth video. Higher resolutions show more detail but need more power to run. Knowing these options helps people choose the best setup for their needs and budget.
For the default 16:9 aspect ratio, encode at these resolutions:
4320p (8k): 7680×4320.
2160p (4K): 3840×2160.
1440p (2k): 2560×1440.
1080p (HD): 1920×1080.
720p (HD): 1280×720.
480p (SD): 854×480.
360p (SD): 640×360.
240p (SD): 426×240.
Understanding 16:9 Resolutions: A Guide to Widescreen Dimensions
The 16:9 aspect ratio has become the standard for displays, from computer monitors and laptops to TVs and smartphones. But what exactly does 16:9 mean, and what are the common resolutions that fall under this aspect ratio?
What is 16:9 Aspect Ratio?
The 16:9 aspect ratio refers to the proportional relationship between the width and height of a display. For every 16 units of width, there are 9 units of height. This creates a rectangular shape that’s wider than it is tall, commonly known as widescreen.
Why is 16:9 So Popular?
The 16:9 aspect ratio gained popularity because it provides a more immersive viewing experience for movies and television shows. It also aligns well with the way our eyes naturally see the world.
Common 16:9 Resolutions
Here’s a breakdown of some common 16:9 resolutions:
| Resolution | Pixels | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| 1280×720 (720p) | 921,600 | HDTV, older computer monitors, some smartphones |
| 1366×768 | 1,049,088 | Laptop screens, entry-level computer monitors |
| 1600×900 | 1,440,000 | Computer monitors, some laptops |
| 1920×1080 (1080p) | 2,073,600 | Full HD TVs, computer monitors, many smartphones |
| 2560×1440 (1440p) | 3,686,400 | High-end computer monitors, some laptops, gaming consoles |
| 3840×2160 (4K) | 8,294,400 | 4K Ultra HD TVs, high-end computer monitors, premium smartphones |
| 7680×4320 (8K) | 33,177,600 | 8K Ultra HD TVs, cutting-edge displays |
Choosing the Right 16:9 Resolution
The best resolution for you depends on your needs and the size of your display. Here are some factors to consider:
- Screen Size: Larger screens generally benefit from higher resolutions to maintain image sharpness.
- Viewing Distance: If you sit closer to the screen, you’ll notice the difference between resolutions more easily.
- Content: If you’re watching high-definition movies or playing games, a higher resolution will provide a better experience.
- Hardware Capabilities: Your computer or device needs to be able to support the resolution you choose.
Beyond 16:9: Other Aspect Ratios
While 16:9 is the most common aspect ratio, there are others to consider:
- Ultrawide (21:9): Offers a more immersive experience for gaming and movies.
- 4:3: An older aspect ratio still found on some displays.
- 1:1: A square aspect ratio sometimes used for social media content.
Key Takeaways
- 16:9 is the standard aspect ratio for most modern displays and video content
- Common 16:9 resolutions range from 720p to 4K, with higher resolutions offering more detail
- Choosing the right resolution balances image quality with device capabilities and viewing needs
Understanding 16:9 Resolutions
The 16:9 aspect ratio has become the standard for most video content and displays. This format offers a wide view that works well for both movies and TV shows.
Evolution and Adoption
The 16:9 ratio started to gain popularity in the 1990s. TV makers and broadcasters wanted a format that could show both old 4:3 content and widescreen movies without wasting screen space.
HDTV helped make 16:9 the main format for TVs and video. By the 2000s, most new TVs came in 16:9. Computer screens soon followed.
Today, 16:9 is used for most video content. It’s the default for YouTube videos, TV shows, and many movies. Most smartphones and tablets also use 16:9 screens or close to it.
Comparison With Other Aspect Ratios
16:9 offers more width than the older 4:3 ratio. This extra space is good for action scenes and landscape shots. It also fits human vision better than 4:3.
Some movies use wider ratios like 21:9. But 16:9 remains more common because it works well for most content. It’s a good middle ground between very wide movie ratios and the squarer 4:3.
For social media, square (1:1) and vertical (9:16) formats have become popular. But 16:9 is still the main choice for horizontal video.
Resolutions Defined
16:9 resolutions are screen sizes that keep the 16:9 shape. Common ones include:
- 1280×720 (720p HD)
- 1920×1080 (Full HD or 1080p)
- 2560×1440 (1440p or QHD)
- 3840×2160 (4K UHD)
Higher numbers mean more pixels and sharper images. 4K (3840×2160) is now common in new TVs and high-end monitors. Some very high-end displays even offer 8K resolution (7680×4320).
For online video, 1080p is often the highest quality offered. 4K is becoming more common but needs fast internet to stream well.
Technical Aspects and Usage
The 16:9 aspect ratio has key technical features that impact its use across different industries. It offers specific resolutions and shapes how content is made and viewed.
True 16:9 Resolutions
True 16:9 resolutions are pixel counts that match the 16:9 ratio exactly. Common ones include 1280×720 (720p), 1920×1080 (1080p), and 3840×2160 (4K). These fit perfectly on 16:9 screens without black bars.
Less common resolutions exist too. 854×480 is used for some non-HD digital TV. 7680×4320 (8K) is an ultra-high resolution for cutting-edge displays.
Picking the right resolution matters. Higher resolutions look sharper but need more processing power. Lower ones work better on older devices.
Industry Impact
The 16:9 ratio changed many industries. TV makers switched from 4:3 to 16:9 screens. This gave viewers a wider picture that matched movies better.
Film studios adapted too. They started framing shots for 16:9 TVs, not just wide theater screens. Some old movies got cropped to fit the new shape.
Video games embraced 16:9 as well. Game designers could show more of the game world at once. User interfaces spread out, becoming easier to read.
Content Creation and Consumption
Content creators now work with 16:9 in mind. Video editors use 16:9 timelines as a default. YouTube recommends 16:9 for uploads, making it the go-to format for online video.
Cameras and phones shoot in 16:9 by default. This lets people capture video that fits modern screens without extra steps.
Viewers expect 16:9 content. When they see other shapes, it often means black bars on the sides or top and bottom. Some find this annoying, pushing creators to stick with 16:9.
Frequently Asked Questions
The 16:9 aspect ratio is common in modern displays. It affects screen dimensions, resolutions, and pixel density. Let’s explore some key questions about this popular format.
What are common screen resolutions that adhere to the 16:9 aspect ratio?
Common 16:9 resolutions include 1920×1080 (1080p), 2560×1440 (1440p), and 3840×2160 (4K). These formats are widely used in TVs, monitors, and smartphones.
720p (1280×720) is also a 16:9 resolution, often found in budget devices.
How does one calculate the dimensions of a 16:9 aspect ratio for various screen sizes?
To find 16:9 dimensions, multiply the screen width by 9 and divide by 16. This gives the height.
For example, a 32-inch wide screen would be 18 inches tall (32 * 9 / 16 = 18).
What is the relationship between resolution and aspect ratio in display technology?
Resolution refers to pixel count, while aspect ratio describes screen shape. A 16:9 screen can have different resolutions, all maintaining the same shape.
Higher resolutions offer more detail within the same aspect ratio.
How can I convert a 9:16 format to a standard 16:9 widescreen format?
To convert 9:16 to 16:9, rotate the content 90 degrees. This changes vertical videos to horizontal.
Cropping may be needed to fit all content in the new format.
Can a resolution of 2560×1440 be classified under the 16:9 aspect ratio?
Yes, 2560×1440 is a 16:9 resolution. It’s known as QHD or 1440p.
This format offers sharp images on larger screens and is popular for gaming monitors.
What are the differences in pixel density between 720p and 1080p resolutions for a 16:9 display?
1080p (1920×1080) has more pixels than 720p (1280×720), leading to higher pixel density.
On the same size screen, 1080p will look sharper. The exact density depends on screen size.




