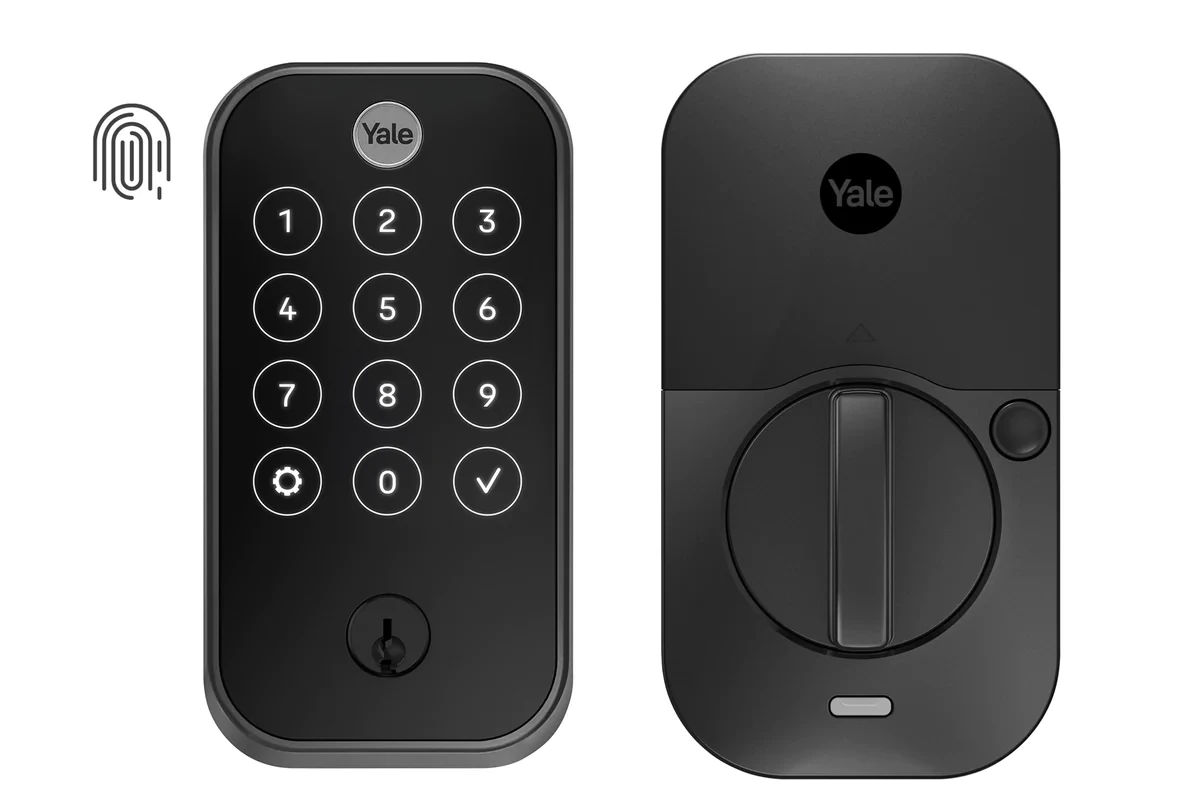
Smart locks have revolutionized home security by offering keyless entry and remote access control through smartphones. They combine traditional lock mechanisms with digital technology, allowing homeowners to manage access without physical keys. While smart locks can be secure when properly installed and maintained, their safety depends on factors like build quality, encryption standards, and how users implement security measures.
Many people worry about hackers breaking into their smart locks, but quality devices from reputable manufacturers include safeguards against digital intrusions. Smart locks are as secure as traditional locks for keeping out random intruders and lazy burglars, while adding convenience features like temporary access codes for visitors or service providers. However, they do have some physical vulnerabilities that traditional locks don’t share.
Smart lock security also depends on how you use them. Regular software updates, strong passwords, and secure Wi-Fi networks all play important roles in keeping your smart lock safe. The best smart locks have built-in safety measures to prevent hacking attempts while offering the convenience of keyless entry.
Are Smart Locks Safe?
Smart locks offer convenience and enhanced control over who can access your home, but many people wonder if they’re truly safe. Like any connected device, they have pros and cons when it comes to security. Here’s an in-depth look at how safe smart locks are and what you need to consider before installing one on your door.
1. How Smart Locks Work
Smart locks use wireless technologies like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or Z-Wave to allow remote locking and unlocking through an app, voice assistant, or key code. Some models also support biometric access like fingerprints.
They often integrate with smart home systems, letting you monitor and control your locks from anywhere, grant temporary access, and get notifications when someone enters or exits.
2. Security Features That Make Smart Locks Safe
- Encrypted Communication: Most smart locks use encryption protocols similar to online banking, ensuring that data sent between your phone and the lock is secure.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Many smart lock apps offer 2FA, adding an extra layer of security beyond just a password.
- Tamper Alerts: Some locks send real-time alerts if someone tries to tamper with them.
- Auto-Lock and Unlock: Automatic locking after a certain time helps prevent accidental security lapses.
- Access Logs: You can view who entered and when, helping you monitor home access.
3. Potential Risks of Smart Locks
- Hacking Risks: Like any device connected to the internet, smart locks can be vulnerable to hackers if they’re not properly secured.
- App Vulnerabilities: If your phone is stolen or your app isn’t protected with a strong password, someone could gain access to your home.
- Power or Connectivity Failures: Smart locks that rely on Wi-Fi or Bluetooth may be temporarily unusable if your network or power goes out—though most have physical key backups or battery power.
- Software Bugs: Poorly maintained software can introduce vulnerabilities if the manufacturer doesn’t regularly release security updates.
4. Tips to Make Smart Locks Safer
- Choose a Reputable Brand: Stick with brands that have a track record for security and provide regular firmware updates.
- Use Strong Passwords: Protect your smart lock app and associated accounts with strong, unique passwords.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Turn on 2FA for any accounts connected to your smart lock.
- Update Regularly: Always keep your lock’s firmware and the controlling app up to date.
- Secure Your Wi-Fi Network: Use a strong password and consider setting up a guest network for your smart devices.
- Have a Backup Plan: Choose a lock that offers a mechanical key override or other backup methods in case of failure.
5. Are Smart Locks Safer Than Traditional Locks?
Both smart locks and traditional locks have vulnerabilities:
- Traditional locks can be picked or bumped by skilled intruders.
- Smart locks can be hacked or fail electronically, but they often offer additional layers of control and monitoring that traditional locks lack.
In many cases, combining a high-quality smart lock with strong security practices makes them just as safe—if not safer—than traditional locks.
Smart locks can be very safe when used correctly and combined with good cybersecurity habits. They offer added convenience, flexibility, and control that traditional locks don’t provide, but they do require responsible management to ensure they remain secure.
Key Takeaways
- Smart locks offer convenience but require proper setup and maintenance to remain secure against both physical and digital threats.
- Quality smart locks from reputable brands include encryption and other security features that protect against most hacking attempts.
- Regular software updates and strong passwords significantly improve smart lock security in home environments.
Understanding Smart Locks
Smart locks blend security with convenience, offering keyless entry and remote control capabilities that traditional locks lack. These electronic devices have revolutionized home security by connecting to smartphones and other smart devices.
Mechanical Vs. Electronic Locks
Traditional mechanical locks use physical components like pins and tumblers that require a matching key to operate. These locks, including common deadbolts, have been reliable for centuries but offer limited functionality.
Electronic smart locks, on the other hand, use digital authentication methods instead of physical keys. They can be unlocked using keypads, fingerprints, smartphones, or voice commands.
While mechanical locks are immune to power outages and hacking attempts, they can be picked or bumped by skilled intruders. Electronic locks eliminate these vulnerabilities but introduce new considerations like battery life and potential connectivity issues.
Many smart locks actually combine both technologies, featuring a traditional keyway as backup alongside the electronic components. This hybrid approach ensures homeowners aren’t locked out during system failures.
Components of Smart Locks
Smart locks typically consist of several key components:
- Lock mechanism: Usually a modified deadbolt or mortise lock
- Control panel: Touchscreen, keypad, or fingerprint scanner
- Connectivity module: Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Z-Wave, or Zigbee chips
- Backup power system: Batteries with low-power alerts
- Backup keyway: Traditional key access (on most models)
The lock mechanism itself is often similar to high-quality traditional locks, providing physical security. The electronic components handle authentication and communication with other devices.
Most smart locks use encrypted communications to prevent digital tampering. Advanced models include tamper alerts that notify homeowners of suspicious activity.
Battery life typically ranges from 3-12 months depending on usage and connectivity options. Many locks send notifications when batteries run low.
Smart Home Compatibility
Modern smart locks integrate seamlessly with broader smart home systems. This allows for automated routines like unlocking doors when you arrive home or locking up at bedtime.
Popular voice assistants like Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri can control compatible smart locks. This hands-free operation proves particularly valuable when carrying groceries or managing children.
The emergence of standardized protocols like Matter is improving cross-platform compatibility. This means newer smart locks can work with multiple ecosystems rather than being limited to one brand.
Smart locks can trigger other connected devices. For example, unlocking your front door might automatically turn on lights, adjust the thermostat, and disarm your security system.
Security cameras often pair with smart locks to record entry events, adding another layer of home protection.
The Advantages of Smart Locks
Smart locks offer significant benefits over traditional locks by combining security with modern technology. They transform how we interact with our homes while providing enhanced control and convenience.
Convenience Features
Smart locks eliminate the need to carry physical keys. Users can lock and unlock doors using their smartphone, making it easier to manage access when away from home. Many models offer automatic locking features that secure your door after a set time period, preventing those “did I lock the door?” moments.
Some smart locks work with voice assistants like Alexa or Google Home, allowing hands-free operation. Others integrate with Apple Watch, letting you control your door with a tap on your wrist.
The elimination of hideaway keys increases security, as burglars often know common hiding spots. Instead, you can use temporary access codes for service providers or visitors.
Many smart locks include features like geofencing, which can automatically unlock doors when you approach with your smartphone and lock them when you leave.
Access Control Management
Smart locks excel at managing who enters your home and when. They allow you to assign individual passcodes to family members, friends, or service providers. This creates an audit trail of who accessed your home.
Most smart locks let you create temporary access codes with specific time windows. For example, you might grant your dog walker access only between 2-4 PM on weekdays.
Through mobile apps, users receive real-time notifications when someone enters or exits. This feature is especially valuable for parents monitoring children arriving home from school or keeping tabs on service workers.
If someone attempts to guess your access code, many smart locks will lock out users after too many failed attempts. This adds a layer of security traditional locks can’t match.
Remote access capabilities allow you to grant entry to unexpected guests even when you’re away from home, offering unprecedented flexibility.
Security Aspects of Smart Locks
Smart locks combine digital technology with traditional locking mechanisms to create a multi-layered security system. When properly implemented, they can offer enhanced protection through encryption, physical safeguards, and real-time monitoring.
Encryption and Cybersecurity
Smart locks rely on encryption to protect digital communications between the lock, your smartphone, and the cloud. Most quality smart locks use AES 128-bit or 256-bit encryption, which is the same standard used by banks and government agencies.
The connection between your phone and lock typically uses Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or Z-Wave protocols. Each has different security profiles:
- Bluetooth: Limited range but generally secure for direct connections
- Wi-Fi: Broader range but requires strong network security
- Z-Wave: Creates mesh networks with encrypted communications
To prevent hacking, manufacturers implement additional protections like two-factor authentication and automatic lockout after multiple failed attempts. Always update your lock’s firmware when available, as these updates often patch security vulnerabilities.
Using strong, unique passwords for your smart lock accounts is essential. Password managers can help create and store complex passwords that are difficult for hackers to crack.
Physical Lock Security
Smart locks must be physically secure in addition to digitally protected. Quality smart locks maintain the same physical security standards as traditional locks, with many offering ANSI Grade 1 or 2 certifications.
Most smart locks include:
- Deadbolt mechanisms resistant to forced entry
- Anti-tamper alerts that notify you of physical interference
- Backup key options for emergency access
Some smart locks have vulnerabilities in their physical components, particularly those with poorly designed housings or exposed screws. Higher-quality models address these concerns with tamper-resistant housings and concealed mounting hardware.
For enhanced physical security, consider models with built-in alarms that trigger during unauthorized access attempts. These systems can integrate with broader home security networks for comprehensive protection.
Monitoring and Alerts
Real-time monitoring represents one of the greatest security advantages smart locks offer over traditional locks. Most smart locks provide:
- Access logs that record who entered and when
- Instant notifications when the door is unlocked
- Remote locking capabilities to secure doors from anywhere
These features allow homeowners to verify who enters their home and when. Many systems can integrate with security cameras for visual confirmation of visitors.
Advanced smart locks also offer temporary access codes for visitors or service providers. These time-limited codes automatically expire after a set period, eliminating the security risks of shared keys.
Some systems can detect suspicious activities, such as multiple failed entry attempts or door ajar conditions. When integrated with home alarm systems, these alerts can trigger broader security responses including contacting monitoring services.
Potential Risks and Vulnerabilities
Smart locks offer convenience but come with security challenges that users should understand. These risks range from digital vulnerabilities to physical weaknesses that could compromise home safety.
Cyber Threats and Hacking Incidences
Smart locks are vulnerable to hacking attempts since they connect to the internet and other devices. Cybercriminals may exploit weak passwords, unpatched software, or insecure Wi-Fi networks to gain unauthorized access.
Many smart locks use Bluetooth or Z-Wave technology, which can be susceptible to signal jamming or interception attacks. In some documented cases, hackers have used replay attacks to capture and reuse authentication signals.
Manufacturers’ security practices vary widely. Some devices lack proper encryption or have outdated firmware with known vulnerabilities. A determined hacker could potentially bypass these digital safeguards.
Security experts recommend:
- Regular firmware updates
- Strong, unique passwords
- Two-factor authentication when available
- Secure home networks with strong encryption
Mechanical Tampering and Lockpicking
Smart locks combine digital and physical components, creating multiple points of vulnerability. The physical lock mechanism can still be susceptible to traditional lockpicking techniques.
Some smart locks have been found to use lower-quality mechanical components than traditional high-security locks. This makes them potentially easier to defeat through physical means like bumping or picking.
Battery compartments on exterior-mounted models may provide access to override mechanisms. An intruder could remove this compartment and trigger emergency access features.
Extreme weather can impact performance in some models. Excessive cold may drain batteries faster, while humidity might affect electronic components.
Despite these vulnerabilities, many smart locks offer additional security features like tamper alerts and audit trails that traditional locks lack. These features can notify homeowners of attempted break-ins and track who accesses the door.
Enhancing Smart Lock Safety
Keeping your smart lock secure requires regular maintenance and smart habits. Taking proactive steps can significantly minimize security risks and protect your home from unauthorized access.
Regular Software Updates
Smart locks rely on software to function properly, making updates crucial for security. Firmware updates often patch security vulnerabilities that hackers might exploit.
Manufacturers regularly release these patches to address newly discovered security issues. Setting up automatic updates ensures the lock always has the latest protection without requiring manual intervention.
Some smart lock systems send notifications when updates are available. Users should never ignore these alerts, as outdated software can leave the lock exposed to various cyber threats.
Many smart locks allow scheduling updates during off-hours to avoid disruption. This feature ensures security doesn’t interfere with daily activities.
Integrating Additional Security Features
Smart locks work best as part of a comprehensive security ecosystem. Combining smart locks with security cameras creates multiple layers of protection for the home.
Video doorbells complement smart locks by allowing homeowners to see who’s at the door before granting access. This visual verification adds another security dimension beyond the digital authentication.
Advanced encryption protects data transmission between the lock and connected devices. Look for locks that use 128-bit encryption or higher for maximum security.
Some systems offer geofencing features that automatically lock doors when authorized users leave a defined area. This prevents doors from accidentally remaining unlocked.
Two-factor authentication adds an extra verification step, making unauthorized access significantly more difficult. Users receive a one-time code on their phone when someone attempts to unlock the door.
Best Practices for Smart Lock Users
Creating strong, unique passwords forms the foundation of smart lock security. Avoid using the same password across multiple devices or accounts.
Regularly reviewing access logs helps identify suspicious activity. Most smart locks maintain detailed records of when the lock was operated and by whom.
Limiting access privileges to trusted individuals reduces potential security risks. The ability to grant temporary access is convenient but should be used carefully.
Consider using a dedicated network for smart home devices separate from the main home network. This network isolation provides additional protection against breaches.
When traveling, users should monitor their smart lock remotely and receive alerts for unusual activities. Most manufacturers offer mobile apps that provide real-time notifications of lock status changes.
Periodic testing ensures the lock functions properly during power outages or connectivity issues. Many models offer backup entry methods like traditional keys or backup batteries.
Smart Lock Integration With Smart Home Systems
Smart locks can connect with other devices in your home to create a seamless security experience. This connectivity allows for greater control and convenience through various platforms and compatible devices.
Working With Smart Assistants
Smart locks work well with popular voice assistants like Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Home. These integrations let you lock or unlock doors using simple voice commands.
“Hey Google, lock the front door” becomes a reality with proper setup. This hands-free control is especially helpful when you’re carrying groceries or have your hands full.
Most leading smart lock brands prioritize compatibility with multiple assistants. This gives you flexibility regardless of which smart ecosystem you prefer.
Voice command security is also addressed in these integrations. Many systems require PIN codes or other verification methods before unlocking doors through voice commands to prevent unauthorized access.
Compatibility With Other Smart Devices
Smart locks can work with other security devices to create a comprehensive home protection system. When someone rings your doorbell camera, you can see who’s there and unlock the door remotely.
Some locks support Matter, a new standard that improves how smart devices work together. This means your lock will likely work with more devices over time.
Automation is another benefit of integration. You can create routines like having all doors automatically lock when you arm your security system or turn off the lights.
Temperature sensors, window sensors, and motion detectors can all communicate with your smart lock. This creates a truly intelligent home that responds to changing conditions.
Evaluating Smart Lock Reliability and Performance
When considering a smart lock for your home, understanding its reliability factors and performance metrics helps ensure you select a product that provides both security and convenience. Several key aspects determine how well these devices function in real-world conditions.
Assessing Long-Term Durability
Smart locks need to withstand daily use and environmental conditions. Most quality models undergo rigorous testing for thousands of lock/unlock cycles to simulate years of operation.
Weather resistance is crucial for exterior installations. Look for locks with an IP rating of at least IP54 for adequate protection against dust and water splashes. Higher-end models often feature IP65 ratings for superior protection.
Battery performance significantly impacts reliability. The best smart locks typically offer:
- 6-12 month battery life with normal use
- Low battery alerts via app notifications
- Emergency backup power options
Physical construction quality matters too. Smart locks are generally more resistant to picking than traditional locks, but only when they use quality components. Metal components tend to outlast plastic ones in critical mechanism areas.
User Feedback and Reviews
Real-world experiences provide valuable insights into smart lock reliability. Professional review sites often conduct extended testing to identify potential issues that may not appear in manufacturer specifications.
Smart locks that aren’t properly maintained can develop problems over time. When examining user reviews, look for comments about:
- Consistency of connectivity (Bluetooth/WiFi reliability)
- Responsiveness of customer support
- Ease of setting up and managing PIN codes
- Software update frequency and quality
Community forums like Reddit discussions on smart lock security often reveal long-term reliability issues not covered in professional reviews. Pay special attention to reports about lock mechanism failures or electronic component issues.
Many users report that PIN code management becomes increasingly important over time. The ability to easily add, remove, and track temporary codes for visitors affects daily usability significantly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Smart locks present both benefits and risks compared to traditional locks. Security experts have identified several common concerns about these devices and how they can be addressed effectively.
What are the potential security vulnerabilities of smart locks compared to traditional locks?
Smart locks connect to networks which creates new security considerations. Unlike traditional locks that can only be bypassed physically, smart locks may be vulnerable to both physical and digital attacks.
Some smart locks may never be as secure as purely mechanical locks due to their electronic components. The digital nature of these locks introduces potential software bugs that could compromise security.
Many smart locks were initially designed for single-family homes, meaning they might not address all security concerns relevant to multi-family buildings or commercial properties.
How can smart locks be compromised by hackers or unauthorized users?
Hackers may attempt to intercept wireless communications between smart locks and their control systems. Weak encryption or outdated firmware can create vulnerabilities that allow unauthorized access.
Some smart locks can be compromised through brute force attacks on their digital interfaces. However, most modern smart locks include lockout features after multiple failed attempts, preventing attackers from simply guessing access codes.
Physical tampering remains a concern for both traditional and smart locks. Some smart locks may be vulnerable to specific types of physical attacks that traditional locks resist better.
What measures do manufacturers take to ensure the security of smart locks?
Manufacturers typically implement multiple layers of security and encryption protocols to protect against unauthorized access. These measures help secure the communication between the lock and connected devices.
Regular firmware updates address security vulnerabilities as they’re discovered. Responsible manufacturers provide these updates automatically or notify users when important security patches are available.
Many smart lock systems include activity logs that record who has accessed the door and when. This tracking feature helps homeowners identify any suspicious activity.
How does the physical durability of smart locks compare to traditional keyed locks?
Smart locks generally offer similar physical durability to traditional locks of comparable quality grades. Many manufacturers use the same physical components as in traditional locks for the mechanical portions.
The electronic components in smart locks do create additional points of potential failure. Circuit boards, motors, and batteries can wear out or malfunction over time.
High-quality smart locks undergo testing for weather resistance, repeated use, and physical attack scenarios. These tests help ensure they can withstand normal wear and environmental conditions.
How do smart locks handle power outages or electronic failures?
Most smart locks include backup power systems or mechanical override options. Some models can operate for months on battery power and provide low-battery warnings well before failure occurs.
Many smart locks have built-in keypad or key cylinder backups that function without power. This redundancy ensures homeowners aren’t locked out during power failures.
Battery-operated smart locks typically maintain their programming during power outages. The lock settings and access codes remain intact even when the power is interrupted.
What are the best practices for maintaining the safety and security of a smart lock system?
Regularly updating firmware and software is essential for security. These updates often patch vulnerabilities that could otherwise be exploited by attackers.
Using strong, unique passwords for smart lock accounts and changing access codes periodically improves security. Avoid using easily guessed codes like birthdays or address numbers.
Integrating smart locks with broader home security technology enhances protection. Combining smart locks with security cameras, alarm systems, and motion sensors creates a more comprehensive security solution.