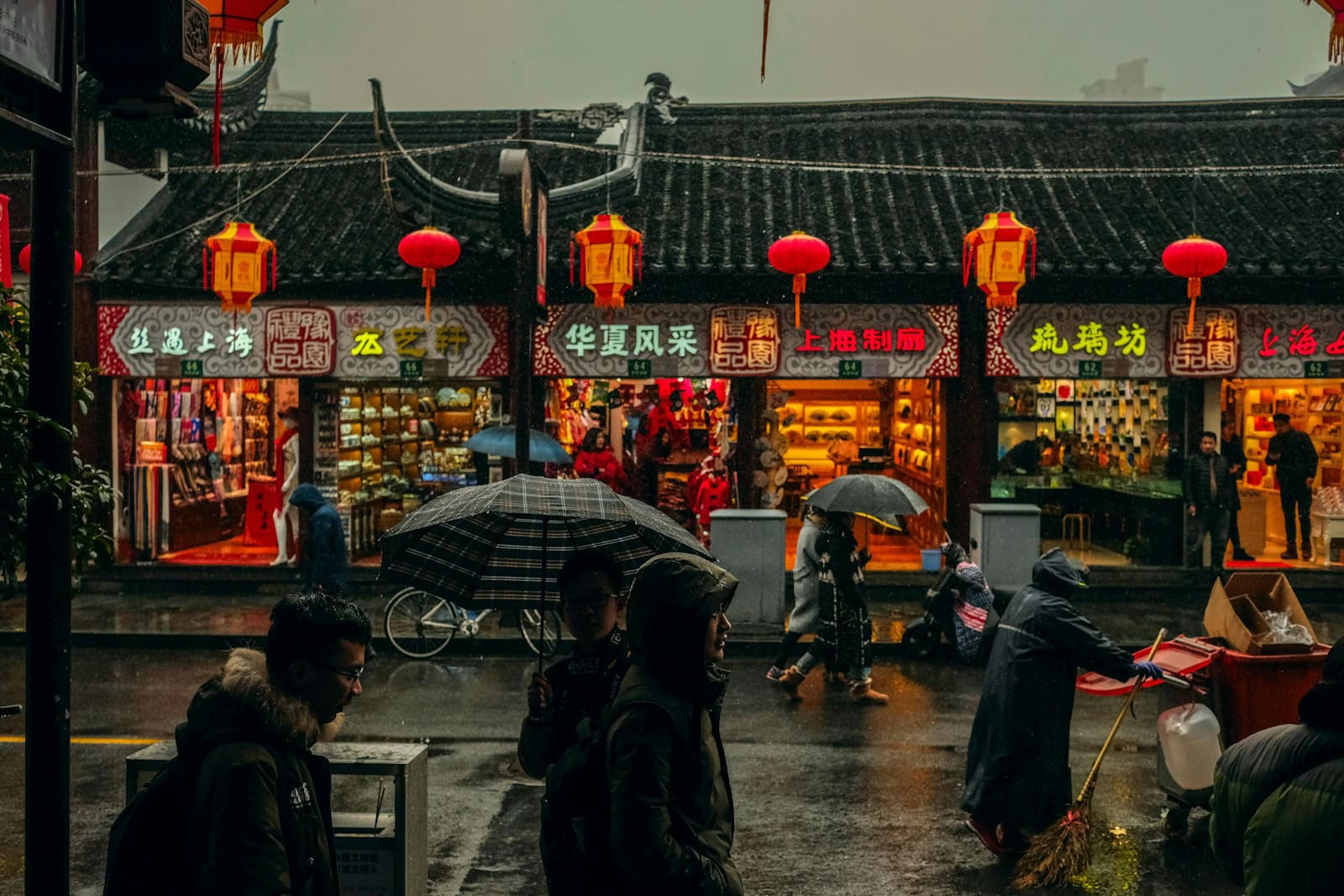
Apple’s strategic approach to AI in China demonstrates a pragmatic adaptation to the unique regulatory landscape. The tech giant has partnered with Chinese e-commerce leader Alibaba to integrate approved AI solutions into iPhones, iPads, and Macs for Chinese users. This collaboration enables Apple to navigate China’s strict data regulations while still delivering AI features to consumers in the world’s largest mobile phone market.
The partnership comes after months of uncertainty about how Apple would roll out its AI features in China. Rather than trying to use its own AI systems, Apple is following Samsung’s example by working with local technology companies. Alibaba is reportedly building an on-device system specifically designed to analyze and modify Apple’s AI models for the Chinese market.
Apple’s CEO Tim Cook’s visit to China aligns with these developments, highlighting the strategic importance of the Chinese market to Apple’s global AI ambitions. This approach reflects Apple’s willingness to adapt its global strategy to meet local requirements, even if it means sharing some control over its AI features with Chinese partners.
Apple’s AI Strategy in China: A Delicate Balancing Act

Apple’s AI Limitations in China
Despite Apple’s push into AI with its Apple Intelligence initiative, the company has faced significant challenges in bringing its AI-powered features to China. The biggest hurdle? Regulations and local competition. China has strict rules governing AI, requiring companies to obtain government approval for large language models and other AI-driven services. Apple, with its privacy-first AI approach, struggled to find a way to comply while maintaining its global brand identity.
Moreover, competitors like Huawei and Xiaomi have been aggressively integrating AI into their devices, giving Chinese consumers local alternatives that are tailored to the market. Unlike Apple, these brands don’t face the same restrictions and can fully leverage cloud-based AI without regulatory roadblocks.
The Alibaba Partnership: Apple’s Solution?
To navigate these challenges, Apple has partnered with Alibaba to bring AI features to iPhones in China. This deal allows Apple to integrate Alibaba’s AI models rather than using its own proprietary AI, which wouldn’t comply with local regulations.
Alibaba, a leader in cloud computing and AI in China, operates large-scale AI models that power services across e-commerce, finance, and cloud infrastructure. By leveraging Alibaba’s AI, Apple can provide AI-powered experiences for iPhone users in China while adhering to government policies.
This approach mirrors how Apple relies on Baidu for maps and search in China instead of using its global Apple Maps and Siri services.
What This Means for iPhone Users in China
For Chinese iPhone users, this partnership could mean:
- More AI-powered features like text generation, voice assistance, and on-device automation.
- Localized AI tools that understand Chinese language and culture better.
- Potentially better integration with Alibaba’s ecosystem, including Alipay, Taobao, and Tmall.
However, it also raises concerns. Since the AI models will be operated by a Chinese company, some users may question whether Apple’s privacy and security commitments remain intact. Apple has historically emphasized on-device processing for privacy, but with Alibaba’s involvement, some AI functions might require cloud processing under China’s regulatory oversight.
Can Apple Regain Its Market Share in China?
Apple has been losing ground in China, with declining iPhone sales as Huawei regains dominance. The Alibaba deal is a strategic move to stay competitive in the world’s largest smartphone market. However, there are no guarantees that it will reverse Apple’s downward trend in China.
The biggest unknown is whether Chinese consumers will find Apple’s AI features compelling enough to choose iPhones over Huawei’s AI-driven smartphones. Huawei has successfully marketed AI-powered photography, voice assistance, and cloud services, positioning itself as the AI leader in China. Apple, on the other hand, is outsourcing its AI rather than building it natively.
The Future of Apple’s AI in China
Apple’s AI strategy in China is a calculated risk. By partnering instead of competing with local tech giants, Apple is playing by China’s rules while ensuring iPhone users still get AI-enhanced experiences.
The key questions that remain:
- Will Apple’s AI features be as seamless as its global offerings?
- Can Apple differentiate itself when Huawei and Xiaomi are already pushing AI-powered innovation?
- Will Chinese consumers trust Apple’s AI when it’s built on Alibaba’s infrastructure?
Apple’s success in China will depend on how well these AI features integrate into the iPhone experience and whether they can compete with local rivals who have full control over their AI technology. If Apple can strike the right balance, this partnership could reshape its future in China.
Key Takeaways
- Apple has partnered with Alibaba to deliver AI features to Chinese iPhone users while complying with local regulations.
- The collaboration involves creating China-specific versions of Apple’s AI models that meet regulatory requirements.
- This strategy follows similar approaches by competitors like Samsung, who partnered with Baidu to offer AI features in China.
Apple’s AI Strategy in the Chinese Market
Apple’s approach to AI in China combines strategic partnerships, regulatory compliance, and market-specific adaptations. The company is working with major Chinese tech firms to develop AI solutions that meet local requirements while expanding its presence in this crucial market.
Adapting to Chinese Consumers
Apple recognizes the distinct preferences of Chinese consumers and is tailoring its AI offerings accordingly. The company is developing specialized AI features for iPhones, iPads, and Macs specifically for the Chinese market. These adaptations reflect Apple’s understanding that global AI solutions cannot simply be transplanted to China without modifications.
Chinese users prioritize different AI applications and have unique usage patterns compared to Western markets. Apple is reportedly enhancing Siri with Baidu’s search capabilities to better serve local search needs. This represents a shift from Apple’s typical one-size-fits-all global product strategy.
The potential is significant, as China’s AI market is projected to reach over $600 billion in annual revenue. Apple’s customized approach aims to capture a share of this growing market while maintaining its premium brand positioning.
Navigating Regulatory Challenges
China’s strict data sovereignty laws and AI regulations present substantial challenges for foreign technology companies. Apple must ensure all AI features comply with local requirements regarding data storage, processing, and content moderation.
Unlike its global AI strategy that integrates OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Apple must develop alternative solutions for China. The company is working with Alibaba to build on-device systems that can analyze and modify Apple’s AI models specifically for Chinese users.
This approach helps Apple address regulatory concerns while still delivering advanced AI capabilities. The company is walking a delicate line between innovation and compliance, strategically positioning itself to maintain market access.
China’s regulatory landscape continues to evolve, requiring Apple to remain flexible and responsive to new requirements while protecting user privacy within the permitted framework.
Importance of Local Partnerships
Apple’s partnerships with Baidu and Alibaba form the cornerstone of its Chinese AI strategy. These collaborations provide Apple with essential local expertise and regulatory compliance capabilities.
Alibaba has emerged as Apple’s primary AI partner in China, developing on-device systems to modify Apple’s AI models for the local market. Meanwhile, Baidu is contributing its search expertise to enhance Siri’s functionality for Chinese users.
These partnerships offer several advantages:
- Regulatory compliance: Local partners understand and navigate China’s complex regulatory environment
- Market knowledge: Chinese tech firms provide insights into local consumer preferences
- Technical capabilities: Partners offer AI expertise specific to Chinese language and culture
Tim Cook’s recent visits to China underscore the importance Apple places on these relationships. By collaborating with multiple Chinese tech giants rather than relying on a single partner, Apple is diversifying its approach and reducing dependence on any one company.
Collaborations and Partnerships
Apple has formed strategic alliances with major Chinese tech companies to navigate the unique regulatory environment for AI deployment in China. These partnerships are essential for Apple to offer AI features on iPhones sold in the Chinese market while complying with local data regulations.
Strategic Alliances with Chinese Tech Giants
Apple has officially partnered with Alibaba to integrate AI features into iPhones sold in China. Alibaba Group Chairman Joe Tsai confirmed this collaboration, which will utilize Alibaba’s Qwen AI model for Apple devices. This arrangement satisfies the Chinese government’s requirement for locally-developed AI models.
The partnership represents a significant opportunity for both companies. For Apple, it provides a compliant way to offer AI capabilities to Chinese consumers amid declining holiday quarter sales. For Alibaba, the deal has boosted investor confidence, resulting in notable stock growth in 2025.
Despite the Alibaba partnership, Apple is simultaneously working with Baidu on AI functionalities. This dual-partnership approach aims to enhance various features including image processing, text capabilities, and an improved Chinese version of Siri.
Research and Development Efforts
Apple’s R&D strategy in China focuses on adapting its Apple Intelligence system to meet local requirements. The company is developing specialized AI features that will be exclusive to devices sold within mainland China.
An important technical distinction exists in how these features are deployed. AI capabilities resulting from these partnerships will only function on Apple devices purchased in China. Devices bought elsewhere and brought into the country won’t have access to these localized AI features.
This region-specific implementation demonstrates Apple’s commitment to creating tailored solutions for different markets. The company is investing considerable resources to ensure its AI offerings meet both regulatory requirements and user expectations in China.
Apple’s collaboration network extends beyond just Alibaba and Baidu, with exploratory discussions with other local tech companies like Xiaomi and Vivo to broaden its AI ecosystem in the region.
Localizing Apple’s AI Offerings
Apple faces unique challenges in bringing its AI services to China. The company is navigating regulatory requirements while adapting its technology to meet local user needs through strategic partnerships.
Tailoring AI Features for the Chinese Audience
Apple plans to expand Apple Intelligence to Chinese users in April 2025, offering simplified Chinese language support. This expansion is part of a broader rollout that includes other languages like French, German, Italian, Portuguese, Spanish, Japanese, and Korean.
The company has partnered with Alibaba to create an on-device system specifically for Chinese users. This collaboration allows Apple to modify its AI models for iPhone, iPad, and Mac users in China.
This partnership represents a strategic approach to address China’s strict data regulations. By working with a local tech giant, Apple can meet compliance requirements that have previously hampered foreign AI systems in the country.
Leveraging Local Data and Insights
Alibaba’s role extends beyond regulatory compliance. The e-commerce giant is building specialized systems to analyze and adapt Apple’s AI models for the Chinese market.
This localization strategy helps Apple sidestep the lengthy regulatory scrutiny typically required for foreign-operated AI systems. The partnership enables enhanced functionality while keeping data processing within China’s borders.
The timing is crucial as Apple faces declining iPhone sales in China. Local competitors like Huawei and Xiaomi have gained market share, making this AI localization effort particularly important.
By leveraging Alibaba’s understanding of local user preferences and data patterns, Apple can create more relevant AI experiences. This approach should help Apple deliver features that resonate better with Chinese consumers while maintaining compliance with local regulations.
Overcoming Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
Apple faces substantial challenges in bringing its AI technologies to the Chinese market. The company must navigate strict government regulations while adapting its products to meet local requirements.
Privacy and Censorship Regulations
China’s regulatory framework for AI technologies is notably stringent. The Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC) has established specific requirements for foreign companies seeking to deploy generative AI tools in the country. These regulations primarily focus on content control and data localization.
Apple must ensure its AI systems comply with Chinese censorship standards that restrict certain topics and expressions. This means modifying Apple Intelligence to filter content according to local regulations.
Data privacy presents another significant challenge. Unlike in Western markets, Apple must store Chinese user data on servers located within China’s borders. The company has previously partnered with GCBD (Guizhou-Cloud Big Data) to manage Chinese iCloud services.
These requirements create a complex balancing act for Apple, which has built its brand on privacy protection. The company must maintain its privacy commitments while satisfying Chinese authorities’ demands for data access and content oversight.
Certifications and Government Relations
Securing proper certifications is essential for Apple’s AI deployment in China. All AI products must receive approval from multiple government agencies before release. This certification process involves technical reviews, security assessments, and content evaluation procedures.
Apple’s CEO Tim Cook has made multiple visits to China in recent months, highlighting the importance of government relations. These high-level engagements aim to navigate regulatory hurdles and establish partnerships with local entities.
The company is reportedly seeking collaborations with Chinese AI firms to meet regulatory requirements. Such partnerships could help Apple integrate its technologies with approved Chinese language models.
Building strong relationships with key regulators like the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) and the CAC is crucial. These connections facilitate the approval process and help Apple stay informed about evolving regulatory expectations.
Success in this area will determine whether Apple can deliver its AI features to the lucrative Chinese market without compromising its core values or global technology standards.
Performance of iPhones in China
Apple’s presence in the Chinese smartphone market has faced significant challenges recently, with fluctuating sales figures and increasing competition from domestic brands amid the company’s AI strategy adjustments.
Market Share Analysis
iPhone sales in China have experienced a downward trend in recent periods. During the first quarter of 2024, Apple’s market share in China declined by approximately 19% year-over-year. This drop positioned Apple as the fifth-largest smartphone vendor in the country, falling behind local competitors.
The decline coincided with the release of the iPhone 15 series, which failed to generate the expected consumer enthusiasm in the Chinese market. Economic factors and stronger competition from local brands contributed to this performance dip.
iPhone 16 sales projections remain cautious, as analysts question whether Apple’s new AI features will help reverse the trend. The company’s inability to immediately implement its full Apple Intelligence suite in China may further impact consumer perception.
Comparison with Chinese Smartphone Brands
Chinese smartphone manufacturers have gained significant advantages over Apple in the local market. Brands like Huawei, Xiaomi, Oppo, and Vivo have captured larger market shares by offering competitive features at lower price points.
Huawei, in particular, has rebounded strongly despite U.S. sanctions, with its Mate series featuring advanced AI capabilities developed domestically. These phones appeal to Chinese consumers who value both patriotic purchasing and cutting-edge technology.
Chinese brands have moved faster in implementing AI features that are tailored specifically for the Chinese market and language. This localization advantage has proven crucial in attracting consumers.
Apple’s partnerships with Alibaba and potential collaborations with Tencent and ByteDance represent attempts to counter this disadvantage. By integrating locally-developed AI models into iPhones sold in China, Apple hopes to offer Chinese users features comparable to those found on domestic smartphones while maintaining its premium positioning.
Advancements in Apple’s AI Hardware and Software
Apple’s approach to artificial intelligence combines powerful hardware innovations with sophisticated software development, creating an ecosystem where AI capabilities are deeply integrated across devices.
Incorporation of AI in Consumer Devices
Apple has positioned its Neural Engine as the cornerstone of its AI strategy across product lines. The Neural Engine, first introduced in the iPhone X, has evolved significantly with each generation of Apple silicon, enabling more complex on-device AI processing capabilities.
Recent iPhone models feature enhanced Neural Engine components that process AI tasks directly on the device rather than relying on cloud servers. This approach prioritizes user privacy while delivering responsive AI features.
The Mac lineup has also received substantial AI hardware upgrades with the transition to Apple silicon. M-series chips include dedicated Neural Engine cores that accelerate machine learning tasks across macOS applications.
Apple’s focus on on-device processing differentiates it from competitors like Google and Amazon, which rely more heavily on cloud-based AI solutions. This strategy reflects Apple’s commitment to privacy as a core design principle.
Development of Proprietary AI Models
Apple has been developing custom AI models optimized specifically for its hardware ecosystem. These models power features like image recognition in Photos, predictive text in Messages, and Siri’s voice recognition capabilities.
The company’s AI development philosophy emphasizes efficiency and performance. Apple’s models are designed to deliver high accuracy while consuming minimal power, a crucial consideration for mobile devices with battery constraints.
Apple Intelligence represents the company’s latest advancement in AI software. This initiative aims to make devices more intuitive and personalized through advanced intelligence technology integrated across the operating system.
While Apple has been more reserved about promoting its AI capabilities compared to some competitors, the underlying technology has been steadily advancing. Each software update introduces more sophisticated AI-powered features that enhance user experience without explicitly highlighting the AI technology powering them.
Apple’s investment plans indicate a significant commitment to AI development, with reports of $500 billion allocated to U.S. operations over the next four years partly supporting continued advances in AI technology.
Corporate Leadership and Vision
Apple’s strategic approach to AI in China is shaped by the leadership decisions and public statements of its executive team. The company faces unique challenges and opportunities in navigating China’s regulatory environment while pursuing innovation.
Tim Cook’s Stance on AI and China
Tim Cook has positioned Apple’s AI strategy in China as a balance between innovation and regulatory compliance. During his visits to China in recent years, Cook has emphasized Apple’s commitment to the Chinese market while acknowledging the need to work within local regulations.
He has met with Chinese officials to discuss Apple’s AI plans and potential partnerships with local companies. The recent collaboration with Alibaba for AI services implementation demonstrates Cook’s pragmatic approach to maintaining Apple’s presence in this critical market.
Cook stated at a 2024 shareholders meeting that Apple views AI as “critical to our future” and that the company is “investing significantly” in this area, including solutions tailored to the Chinese regulatory environment.
Key Statements at International Forums
At the World Governments Summit in Dubai, Tim Cook outlined Apple’s vision for AI that respects user privacy while delivering innovative features. He emphasized that Apple would take a measured approach to AI deployment across global markets, including China.
“We believe in thoughtful innovation that considers both technological advancement and cultural context,” Cook remarked during the summit. This philosophy has guided Apple’s decision to partner with Alibaba for its AI rollout in China.
Joe Tsai, Alibaba’s chairman, joined Cook at the China Development Forum where they discussed the power of partnerships in navigating complex regulatory environments. Their public statements highlighted the mutual benefits of collaboration between American technology companies and Chinese partners.
The Competitive Landscape
Apple’s AI strategy in China faces intense competition from local tech firms and smartphone manufacturers. The tech giant must navigate both regulatory challenges and market pressures as it attempts to deploy AI features in this crucial market.
Rivalry with Domestic Smartphone Manufacturers
Chinese smartphone brands like Huawei have experienced a strong resurgence, directly challenging Apple’s market position. Local competitors have aggressively integrated advanced AI capabilities into their devices, creating products that appeal to tech-savvy Chinese consumers.
Huawei’s comeback has been particularly notable, with its AI-enhanced devices gaining significant traction. Other domestic rivals such as Xiaomi, Oppo, and Vivo continue to expand their AI offerings, frequently launching new features before they appear on iPhones.
Market share figures reflect this changing landscape. Apple’s inability to launch its Apple Intelligence platform in China has created an opportunity for domestic manufacturers to highlight their AI superiority.
Evaluating Apple’s Position in the AI Race
Apple’s approach to AI in China involves forming strategic partnerships with local companies. The company has selected Alibaba as its AI partner to help navigate regulatory requirements and launch AI features in the Chinese market.
This collaboration reflects the reality that foreign companies face significant regulatory hurdles from China’s Cyberspace Administration. Without such partnerships, Apple cannot deploy generative AI features that have become increasingly important to smartphone buyers.
Analysts expect Apple’s recent $500 billion investment in U.S. operations may have limited impact on its Chinese prospects. The competitive dynamics in China demand more focused regional strategies.
The iPhone 16 launch in China reportedly failed to generate enthusiasm among consumers seeking advanced AI capabilities. This tepid reception highlights how crucial AI features have become in the world’s largest smartphone market.
Apple’s AI Initiatives in E-commerce
Apple is expanding its AI strategy in the Chinese market through strategic partnerships with e-commerce giants. These collaborations aim to integrate Apple’s AI features into the shopping experience while navigating China’s regulatory environment.
Collaboration with E-commerce Giants
Apple has formed a significant partnership with Alibaba Group to bring its AI services to the Chinese market. This alliance allows Apple to bypass lengthy regulatory scrutiny required for foreign-operated AI systems in China. The collaboration was announced as Apple faced declining revenues in the Greater China region, with recent reports showing an 11% year-on-year drop to $18.5 billion.
Alibaba, whose advances in artificial intelligence have boosted its shares by more than 40% this year, will serve as Apple’s primary AI partner in China. This partnership removes months of uncertainty for the Cupertino-based company about how it would deploy its AI features in the world’s largest mobile phone market.
Enhancing Online Retail With AI
The Apple Intelligence initiative aims to integrate AI capabilities across Apple’s product range in the e-commerce space. These features promise to transform how Chinese consumers shop online using Apple devices. The AI enhancements will include improvements to Siri that could facilitate easier product searches and purchases.
New capabilities will also help users automatically organize shopping-related emails and information. This could create a more seamless shopping experience for consumers using iPhones and other Apple devices in China’s robust e-commerce ecosystem.
The partnership strategy demonstrates Apple’s adaptability in different markets. By leveraging local expertise through Alibaba, Apple can deliver enhanced AI functionality while respecting China’s regulatory framework and potentially reversing its recent sales decline in the region.
Challenges and Opportunities
Apple faces significant hurdles in China’s AI landscape while also seeing potential growth avenues. The company must navigate complex regulatory requirements and strong local competition while maintaining its privacy-focused approach.
Anticipating Future AI Trends
Apple’s privacy-first approach creates unique challenges in China’s AI development ecosystem. Unlike competitors who freely share user data, Apple limits data collection, putting it at a disadvantage when training large language models that require massive datasets.
Regulatory hurdles present another obstacle. China maintains stringent rules for AI systems, especially those operated by foreign companies. This regulatory environment forces Apple to pursue local partnerships rather than deploying its own AI solutions.
Competition from domestic players like Baidu and Huawei intensifies the challenge. Chinese companies have advanced AI capabilities and better understand local user preferences and regulatory requirements.
To address these issues, Apple has partnered with Baidu for AI services in China. Apple covers training costs while Baidu allocates cloud resources and increases chip investments to handle Apple users’ AI requests.
Potential for Growth in AI Integration
Despite challenges, Apple has significant opportunities to expand its AI presence in China. Strategic partnerships allow Apple to sidestep lengthy regulatory scrutiny while delivering enhanced functionality to Chinese users.
The collaboration with Baidu represents a promising approach. This partnership enables Apple to maintain its privacy standards while accessing local AI expertise and infrastructure. Baidu’s increasing investment in cloud resources specifically for Apple signals potential for substantial growth.
Apple can differentiate itself by focusing on on-device AI processing, which aligns with its privacy philosophy and may appeal to privacy-conscious Chinese consumers. This approach could create a unique selling proposition in a market dominated by cloud-based AI solutions.
The company might also explore specialized AI applications in areas like photography, health monitoring, and personalized services that don’t require extensive data sharing. These targeted implementations could showcase Apple’s AI capabilities without compromising its core privacy principles.
Frequently Asked Questions
Apple’s approach to AI in China involves complex regulatory navigation, strategic partnerships, and market-specific technologies to maintain its competitive edge in one of its largest markets.
What AI technologies has Apple implemented specifically for the Chinese market?
Apple has developed region-specific AI features for the Chinese market to overcome regulatory hurdles. These technologies focus on maintaining user privacy while delivering functionality that meets local requirements.
The company has explored on-device processing for certain AI features to comply with data sovereignty regulations. This approach allows Apple to offer AI capabilities without sending user data to servers outside China.
Apple’s China-specific AI implementations include modifications to voice recognition algorithms that better understand Chinese dialects and accents.
How is Apple adapting its AI capabilities to comply with China’s regulatory environment?
Apple has pursued partnerships with Chinese tech companies to navigate the country’s regulatory landscape. The collaboration with Alibaba represents a strategic move to offer AI features while meeting China’s data localization requirements.
Data storage for Apple’s AI services in China is handled through local data centers. This approach ensures compliance with China’s cybersecurity laws that require certain types of data to remain within national borders.
The company has engaged in ongoing discussions with Chinese regulators to find acceptable frameworks for implementing Apple Intelligence features in the region.
What are the strategic goals of Apple’s AI development in China?
Apple aims to regain market share in China through AI innovation. The company reported an 11% decline in revenue from Greater China in a recent quarter, partly attributed to the lack of Apple Intelligence availability in the country.
Enhancing user experience for Chinese consumers represents another key strategic goal. By providing AI features tailored to local preferences, Apple hopes to increase device stickiness and ecosystem loyalty.
Long-term competitive positioning against domestic manufacturers like Xiaomi and Huawei, who offer advanced AI capabilities, remains a primary motivation for Apple’s AI investments in China.
How does Apple’s approach to AI in China compare to its global AI strategy?
Apple’s global AI strategy emphasizes privacy and on-device processing, while its China approach requires more flexibility and local partnerships. This creates a dual-track development path that balances global principles with local requirements.
In most markets, Apple maintains tight control over its AI ecosystem. In China, the company has shown willingness to integrate third-party AI technologies from companies like Alibaba.
The level of transparency regarding data handling differs between Apple’s global and China-specific AI implementations. Chinese operations must adhere to local data access laws that may conflict with Apple’s privacy standards elsewhere.
What partnerships has Apple formed to advance AI research and applications in China?
Apple has partnered with Alibaba to bring AI features to iPhones in China. This collaboration leverages Alibaba’s local market expertise and AI capabilities while utilizing Apple’s hardware excellence.
Reports indicate Apple has explored potential partnerships with Tencent and ByteDance. These discussions focus on integrating their AI models into iPhones sold in China to provide local generative AI services.
Apple previously negotiated with Baidu for AI integration but faced challenges related to data security concerns. The company has reportedly agreed to cover costs for training AI models while Baidu allocates cloud resources and increases chip investments.
How has Apple’s AI technology impacted consumer behavior in China?
Chinese consumers have shown increasing interest in AI-powered smartphone features. Apple’s delayed implementation of advanced AI capabilities has influenced some users to consider alternative brands with more robust AI offerings.
The integration of AI services tailored to Chinese users creates new interaction patterns. Voice assistants that better understand local dialects and cultural references encourage more frequent engagement with Apple devices.
Privacy concerns remain important to Chinese iPhone users. Apple’s reputation for data protection gives it a potential advantage even as it adapts its AI approach to meet local regulatory requirements.