A bad IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) number can cause significant problems for smartphone users. A bad IMEI means the device has been reported as lost, stolen, or associated with fraudulent activity, resulting in its blacklisting by mobile carriers. This unique 15-digit code identifies each mobile device and plays a crucial role in network connectivity.
Checking your device’s IMEI status is simple. Users can dial *#06# on their phone’s keypad or find it in the settings menu under “About Phone.” Online IMEI checkers also provide a quick way to verify a device’s status before purchase or troubleshoot connectivity issues.
A blacklisted IMEI can render a phone unusable on certain networks. This security measure helps prevent stolen devices from being activated. However, legitimate owners may face challenges if their phone is mistakenly blacklisted or they purchase a second-hand device with an unknown history.
Understanding Bad IMEI
IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) is a unique 15-digit number that identifies your mobile device. It’s like a digital fingerprint for your phone. A bad IMEI can cause various problems, including:
1. Network Connectivity Issues
- Your device may not be able to connect to a mobile network.
- You may experience dropped calls or poor call quality.
- You may not be able to send or receive text messages.
2. Inability to Update Software
- You may not be able to download and install software updates for your device.
3. Device Blocking
- Your device may be blocked by your carrier or by authorities if it has been reported lost or stolen.
4. Reduced Resale Value
- A device with a bad IMEI may be difficult to sell or trade in.
Causes of a Bad IMEI
- Incorrect IMEI entered during manufacturing: This is rare but can happen.
- Software corruption: Malware or other software issues can corrupt the IMEI.
- Hardware damage: Damage to the device’s motherboard or other components can affect the IMEI.
- Lost or stolen device: Carriers may blacklist the IMEI of lost or stolen devices.
What to Do if You Have a Bad IMEI
- Contact your carrier: They may be able to help you troubleshoot the issue or provide a replacement device.
- Contact the manufacturer: If the issue is due to a manufacturing defect, the manufacturer may be able to repair or replace your device.
- Avoid buying used devices with bad IMEIs: Always check the IMEI of a used device before purchasing it.
Key Takeaways
- A bad IMEI indicates a device has been reported lost, stolen, or linked to fraud
- IMEI numbers can be easily checked using phone settings or online tools
- Blacklisted IMEIs may prevent device activation on mobile networks
Understanding IMEI and Its Importance
IMEI numbers play a crucial role in mobile device identification and security. These unique codes help track phones and protect users from theft or fraud.
Basics of IMEI
IMEI stands for International Mobile Equipment Identity. It is a 15-digit code assigned to each mobile device. This number acts as a digital fingerprint for smartphones and tablets.
Every IMEI is unique worldwide. Users can find their IMEI by dialing *#06# on their phone’s keypad. The number will appear on the screen.
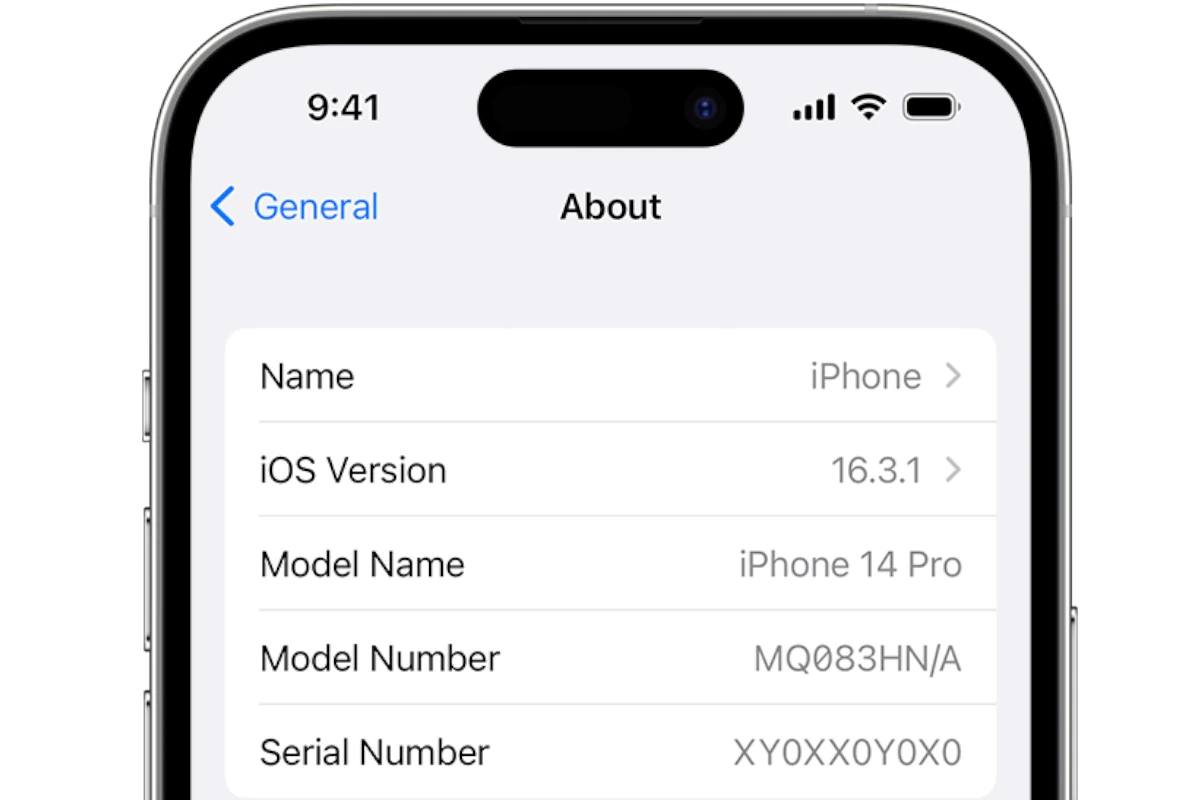
IMEI codes are also printed inside the battery compartment or on the SIM tray of most devices. For iPhones, users can check Settings > General > About to view the IMEI.
Role of IMEI in Mobile Networks
Mobile operators use IMEI numbers to identify devices on their networks. This helps them manage connections and provide services efficiently.
IMEI codes allow carriers to:
- Block stolen phones from accessing networks
- Identify device models and specifications
- Track warranty information
- Assist in locating lost or stolen devices
Carriers store IMEI data in Equipment Identity Registers (EIRs). These databases help prevent the use of unauthorized or stolen devices on their networks.
IMEI numbers work on both GSM and CDMA networks. They enable global device tracking and identification across different mobile technologies and regions.
Consequences of a Bad IMEI
A bad IMEI can severely restrict a mobile device’s functionality and create legal issues for its owner. This unique identifier plays a crucial role in how phones interact with cellular networks.
Blacklisting Reasons
Mobile carriers and law enforcement agencies may blacklist IMEI numbers for several reasons. Theft is a primary cause, with stolen phones quickly added to blocklists. Unpaid bills or contract breaches can also lead to blacklisting. Some countries blacklist imported phones that haven’t paid proper taxes or don’t meet local regulations.
Carriers share IMEI blacklists through central databases. This cooperation helps prevent stolen devices from being used on other networks. In some cases, phones with modified IMEI numbers may be blacklisted if detected.
Impact on Usability
A bad IMEI significantly limits a phone’s usability. The device cannot connect to cellular networks, making calls or sending texts impossible. Data services become unavailable, cutting off internet access through mobile networks.
Changing SIM cards or switching carriers won’t resolve the issue. The IMEI is tied to the device itself, not the SIM. Some features may still work over Wi-Fi, but core cellular functions remain blocked.
Selling or transferring a blacklisted phone is often illegal. Attempting to modify the IMEI is also against the law in many countries. Users with blacklisted phones must contact their carrier or relevant authorities to resolve the issue legitimately.
Identifying and Checking IMEI Status
IMEI numbers serve as unique identifiers for mobile devices. Knowing how to find and check your IMEI status can help verify a phone’s legitimacy and history.
How to Find Your IMEI
The IMEI number is typically a 15-digit code. On most Android phones and iPhones, you can find it by dialing *#06# on the keypad. The number will appear on the screen.
For Android devices, you can also locate the IMEI in the Settings app:
- Go to Settings
- Select “About Phone”
- Tap on “Status” or “IMEI information”
iPhone users can find the IMEI in Settings:
- Open Settings
- Tap “General”
- Select “About”
The IMEI is often printed on the SIM card tray or behind the battery on some phone models.
Using IMEI Checking Services
Several online services allow you to check the status of an IMEI number. These tools can reveal if a phone has been reported lost, stolen, or blacklisted.
IMEI.info is a free service that provides basic information about a device. It can confirm the phone’s make and model.
CheckMEND offers more detailed reports, including theft and loss records. This service usually charges a fee.
Mobile carriers often have their own IMEI checking tools on their websites. These can verify if a phone is compatible with their network.
When buying a used phone, an IMEI check is crucial. It helps ensure the device isn’t stolen or blocked by a carrier.
Preventative Measures and Solutions
Protecting your phone’s IMEI and addressing bad IMEI issues are crucial for maintaining cellular services and device security. Taking proactive steps can prevent problems and resolve existing IMEI-related issues.
Preventing IMEI-Related Issues
Register your device with your mobile operator. This helps prove ownership if the phone is lost or stolen. Enable security features like Google Find My Device to track and remotely lock your phone. Use strong passwords and biometric locks to prevent unauthorized access.
Keep your IMEI number private. Don’t share it online or with strangers. When selling a used phone, verify the buyer’s identity and complete the transaction in a safe location. Consider using an eSIM instead of a physical SIM card to reduce the risk of SIM swapping attacks.
Avoid purchasing phones from unlicensed sellers or suspicious sources. These devices may have bad IMEIs. Always check a phone’s IMEI status before buying. Use reputable IMEI checking services to verify if a device is clean.
Dealing with a Bad IMEI
If your phone has a bad IMEI, contact your carrier immediately. They may be able to unblock the IMEI if it was mistakenly blacklisted. Provide proof of ownership and purchase documents to support your case.
For phones with permanently blacklisted IMEIs, options are limited. Some repair shops offer IMEI repair services, but these are often illegal and unreliable. It’s best to avoid such practices.
Consider selling the device for parts through reputable services like TechPayout. Alternatively, use the phone for Wi-Fi-only functions or as a backup device. In most cases, replacing the blacklisted phone with a new, clean IMEI device is the safest and most reliable solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
IMEI numbers play a crucial role in identifying mobile devices. Understanding the implications of a bad IMEI can help users navigate potential issues with their phones.
How can I check if an IMEI number is blacklisted?
Several online tools allow users to check IMEI status. Websites like IMEI.info or carriers’ official portals often provide this service. Users can enter their 15-digit IMEI number to see if it’s blacklisted.
Mobile network operators also offer IMEI checking services. Contacting customer support or visiting a carrier store can provide accurate information about an IMEI’s status.
Are there any legal implications to selling a phone with a bad IMEI?
Selling a phone with a bad IMEI can lead to legal trouble. In many jurisdictions, it’s illegal to knowingly sell stolen or blacklisted devices. Sellers may face fines or criminal charges.
Buyers who unknowingly purchase phones with bad IMEIs may have legal recourse against sellers. Consumer protection laws often cover such transactions.
What options are available to unlock a phone with a bad IMEI?
Unlocking a phone with a bad IMEI is challenging and often not possible through legitimate means. Some users attempt to change the IMEI, but this is illegal in many countries.
Contacting the original carrier or previous owner may help resolve the issue if the IMEI was blacklisted by mistake. In some cases, paying off outstanding balances can remove a blacklisting.
What consequences arise from using a phone with a blacklisted IMEI number?
Using a phone with a blacklisted IMEI can result in service interruptions. Carriers may block the device from connecting to their networks.
Users may face difficulties activating new service plans or switching carriers. Some features, like emergency calls, might still work despite the blacklisting.
Is it possible to trade in a phone with a blacklisted IMEI at official retailers?
Official retailers typically don’t accept phones with blacklisted IMEIs for trade-ins. These devices have little to no value in legitimate markets.
Attempting to trade in such a device may lead to rejection or, in some cases, investigation into the phone’s origin.
What are potential solutions for a non-working IMEI on a smartphone?
A non-working IMEI often indicates a software or hardware issue. Performing a factory reset might resolve software-related IMEI problems.
For hardware issues, professional repair services may be able to fix the IMEI. In some cases, replacing the device’s motherboard can restore IMEI functionality.