Overclocking is the process of increasing a computer component’s speed beyond its default settings. This technique can boost performance, especially for CPUs and GPUs, allowing systems to run faster without buying new hardware. Many enthusiasts and gamers use overclocking to get more power from their existing setups.
While overclocking can provide noticeable gains, it also comes with risks. Pushing components too hard may lead to instability, crashes, or even hardware damage. Proper cooling becomes crucial when running parts at higher speeds, as they generate more heat. Users must balance the potential benefits against these drawbacks.
Successful overclocking requires careful testing and adjustment. Gradually increasing clock speeds and voltages helps find the sweet spot between performance and stability. Specialized software tools assist in monitoring temperatures and running stress tests to ensure the system remains reliable under load.
Overclocking Demystified: A Beginner’s Guide
Overclocking is like turning up the dial on your computer’s hardware to make it run faster. It involves increasing the clock speed of your CPU, GPU, or RAM beyond the manufacturer’s default settings. This can lead to significant performance gains in games and other demanding applications. However, it’s important to understand the process and potential risks before you start.
Understanding Clock Speed
Clock speed is the rate at which a processor executes instructions. It’s measured in gigahertz (GHz). A higher clock speed means the processor can perform more calculations per second, resulting in faster performance.
Why Overclock?
Overclocking can provide a noticeable boost in performance, especially in CPU-intensive tasks like gaming and video editing. It can also help you squeeze extra life out of older hardware.
Risks and Considerations
Overclocking isn’t without risks. Pushing your hardware too far can lead to:
- Instability: Your system might become unstable, resulting in crashes or errors.
- Overheating: Overclocking generates more heat, which can damage components if not properly managed.
- Reduced lifespan: While generally not a major concern, overclocking can potentially shorten the lifespan of your components.
- Voided warranties: Overclocking might void your warranty, so proceed with caution.
How to Overclock
The overclocking process varies depending on the component you’re overclocking and your system’s motherboard and BIOS. Here’s a general overview:
- Check your hardware: Make sure your CPU, GPU, and motherboard support overclocking.
- Update your BIOS: Ensure your BIOS is up to date to access the latest overclocking features.
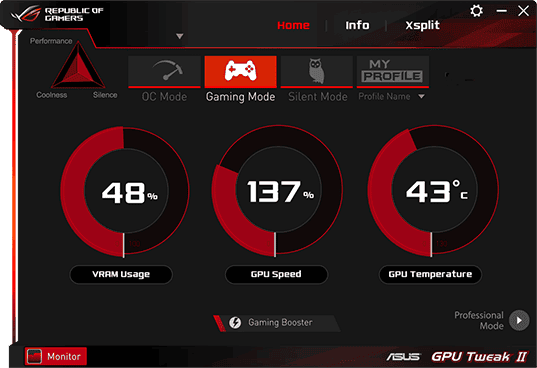
- Monitor temperatures: Use monitoring software to track your component temperatures during overclocking.
- Increase clock speed gradually: Make small adjustments to the clock speed and test for stability.
- Stress test: Use stress testing software to ensure your system remains stable under load.
- Adjust voltage (if needed): Increasing voltage can provide more headroom for overclocking but also increases heat generation.
Essential Tools
- BIOS: Your motherboard’s BIOS provides settings for adjusting clock speeds and voltages.
- Monitoring software: Tools like CPU-Z, GPU-Z, and HWMonitor allow you to monitor temperatures and other system parameters.
- Stress testing software: Prime95, FurMark, and Memtest86 are commonly used for stress testing.
Tips for Safe Overclocking
- Start small: Make small adjustments to clock speeds and test for stability before making further increases.
- Monitor temperatures closely: Keep an eye on your component temperatures to prevent overheating.
- Use adequate cooling: Ensure your system has sufficient cooling to handle the increased heat generated by overclocking.
- Back up your data: It’s always a good idea to back up your data before making any significant system changes.
- Know your limits: Don’t push your hardware too far. Overclocking is about finding a stable balance between performance and stability.
Overclocking Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Increased performance | Potential instability |
| Enhanced gaming experience | Risk of overheating |
| Extended lifespan of older hardware | Possible reduced component lifespan |
| Cost-effective performance boost | May void warranty |
Overclocking can be a rewarding way to unlock extra performance from your PC. However, it’s important to approach it with caution and understand the potential risks. By following best practices and using the right tools, you can safely overclock your hardware and enjoy the benefits of increased performance.
Key Takeaways
- Overclocking increases component speeds for better performance
- Proper cooling and careful testing are essential for safe overclocking
- Users must weigh potential gains against risks like instability or hardware damage
Understanding the Basics of Overclocking
Overclocking boosts a computer’s speed by tweaking key components. It’s a way to get more power from your hardware, but it requires care and knowledge to do safely.
Defining Overclocking and Its Purpose
Overclocking makes computer parts run faster than their default settings. It focuses on the CPU, GPU, and RAM. The main goal is to increase processing speed and improve performance in tasks like gaming or video editing.
Users can push their hardware beyond factory limits. This can lead to noticeable gains in speed and responsiveness. For example, a CPU might finish calculations quicker or handle more tasks at once.
Overclocking is popular among tech enthusiasts and those who want top performance without buying new parts. It’s a cost-effective way to extend a computer’s life or boost its capabilities.
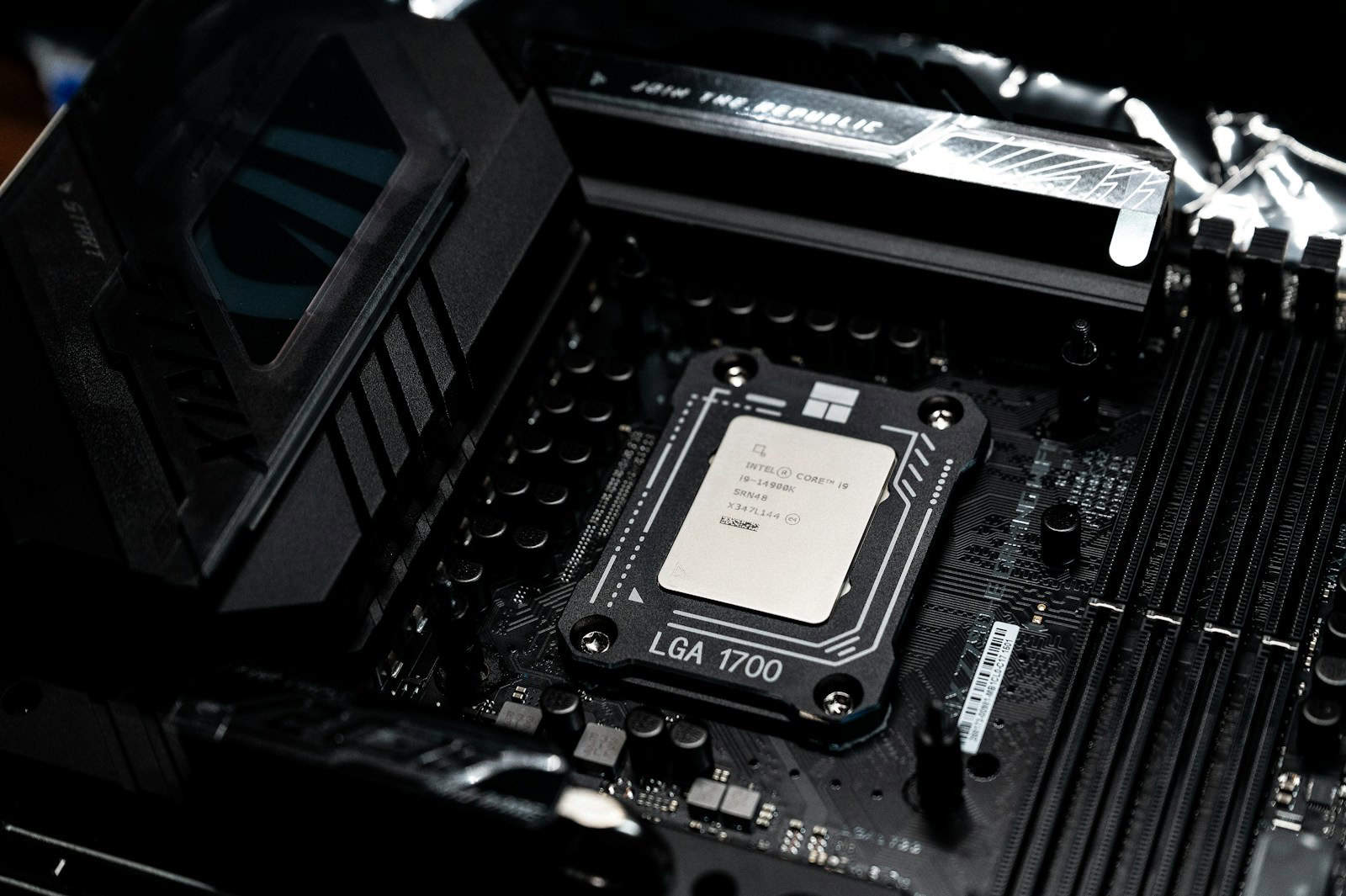
The Role of the CPU in Overclocking
The CPU is often the main target for overclocking. Its speed is measured in GHz, which shows how many cycles it can do per second. Overclocking raises this number.
Two key factors affect CPU speed: base clock (BCLK) and multiplier. The BCLK is the basic timing of the system. The multiplier increases this base value to set the final CPU speed.
For instance, a 100 MHz BCLK with a 40x multiplier results in a 4 GHz CPU speed. Overclocking might raise the multiplier to 45x, creating a 4.5 GHz speed.
Changing these values can boost performance, but it also increases heat and power use. Proper cooling is crucial to keep the CPU stable at higher speeds.
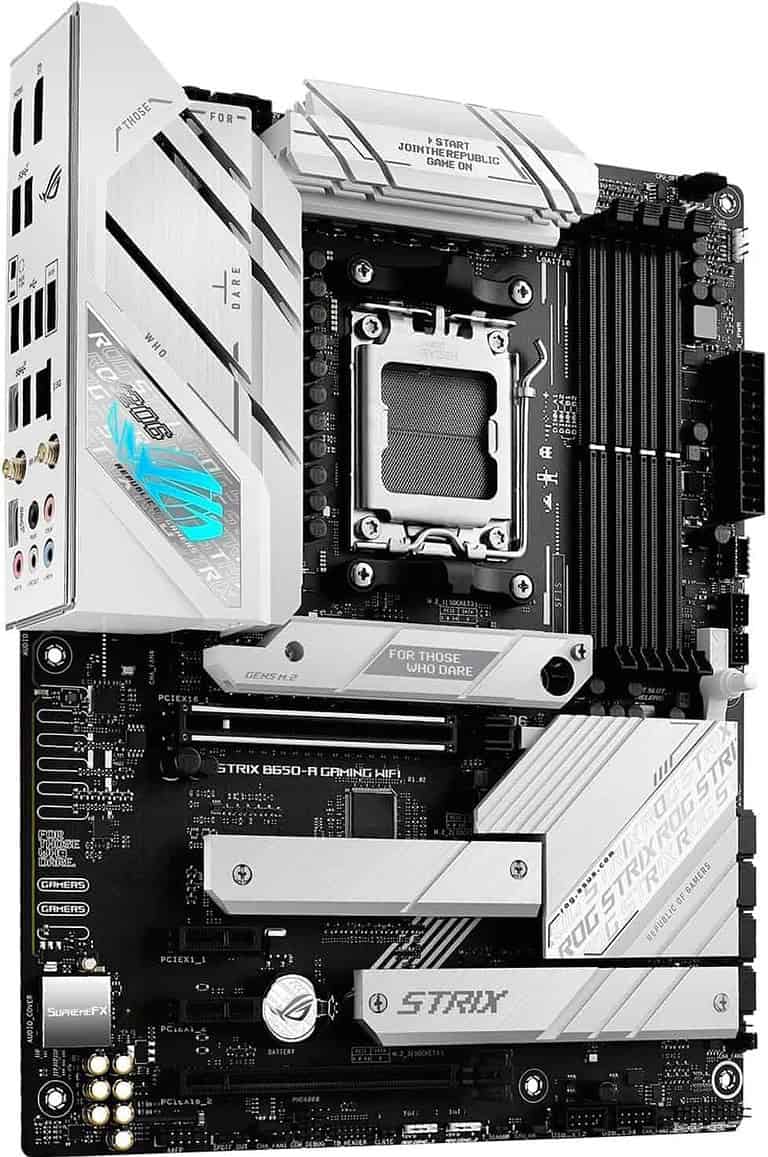
Motherboard and BIOS Configuration
The motherboard and BIOS play vital roles in overclocking. They control power delivery and allow users to change key settings.
BIOS settings let users adjust CPU voltage, frequency, and other parameters. These changes are crucial for stable overclocking.
Some key BIOS settings for overclocking include:
- CPU multiplier
- Base clock
- CPU voltage (Vcore)
- Memory frequency and timings
Not all motherboards support overclocking. High-end models often have better power delivery and more options for tweaking.
Users should research their specific motherboard and CPU to find safe overclocking limits. Small, gradual changes are safer than big jumps in speed or voltage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Overclocking involves several key aspects that users often have questions about. These include performance impacts, potential risks, and the overclocking process itself for various components.
How does overclocking impact CPU performance?
Overclocking a CPU can boost its speed and processing power. It allows the processor to handle more tasks per second. This can lead to faster program execution and improved multitasking abilities. The performance gains vary depending on the specific CPU model and the extent of overclocking applied.
What are the risks associated with overclocking a GPU?
GPU overclocking carries some risks. It can cause system instability if not done correctly. Overheating is a major concern, as higher clock speeds generate more heat. This may lead to graphics glitches or system crashes. In extreme cases, it could potentially damage the GPU. Proper cooling and careful voltage management are essential to minimize these risks.
Can laptop components be safely overclocked, and if so, how?
Laptop overclocking is possible but requires extra caution. Most laptops have limited cooling capacity compared to desktop PCs. This makes heat management more challenging. Some high-end gaming laptops offer built-in overclocking tools. These are generally safer to use as they are designed for that specific hardware. For other laptops, it’s best to stick to modest overclocks and monitor temperatures closely.
What are the potential consequences of overclocking RAM on system stability?
RAM overclocking can affect system stability in several ways. It may cause random crashes or freezes if pushed too far. Data corruption is another risk, especially during file transfers or system updates. In some cases, it can lead to boot failures. The system may become unstable even at stock speeds if the overclock is not properly configured.
How can one determine if their PC components are currently overclocked?
There are several ways to check if components are overclocked. For CPUs, software like CPU-Z can show current clock speeds. GPU overclocking can be checked through tools like MSI Afterburner. BIOS settings also often display current clock speeds for various components. Some motherboards have LED indicators that show when XMP profiles are active for RAM.
What steps are involved in the overclocking process for hardware components?
The overclocking process typically involves several steps. First, enter the BIOS or use specialized software for the component. Gradually increase the clock speed in small increments. Test stability after each change using stress test software. If stable, repeat the process until desired performance is reached or instability occurs. Adjust voltages as needed, but with caution. Finally, implement proper cooling solutions to manage the increased heat output.