Microsoft Mobile Device Management (MDM) offers businesses a powerful solution for securing and controlling mobile devices in their networks. This technology allows organizations to protect company data, enforce security policies, and manage applications across various devices.
Microsoft Intune, a key component of Microsoft’s MDM strategy, enables IT administrators to manage both company-owned and personal devices used for work. It provides a comprehensive set of tools for device enrollment, policy creation, and remote management. This cloud-based service integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products, offering a unified approach to endpoint management.
MDM solutions like Microsoft’s are becoming essential as more employees use personal devices for work tasks. They help organizations balance security needs with user privacy, ensuring that company data remains protected without infringing on personal information stored on devices. Microsoft’s MDM offerings cater to businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large enterprises, with scalable and customizable features.
Microsoft Mobile Device Management Solutions
Microsoft offers a comprehensive suite of mobile device management (MDM) solutions to help organizations secure and manage their mobile devices. These solutions provide businesses with the tools they need to protect corporate data, ensure compliance, and empower employees to work from anywhere, on any device.
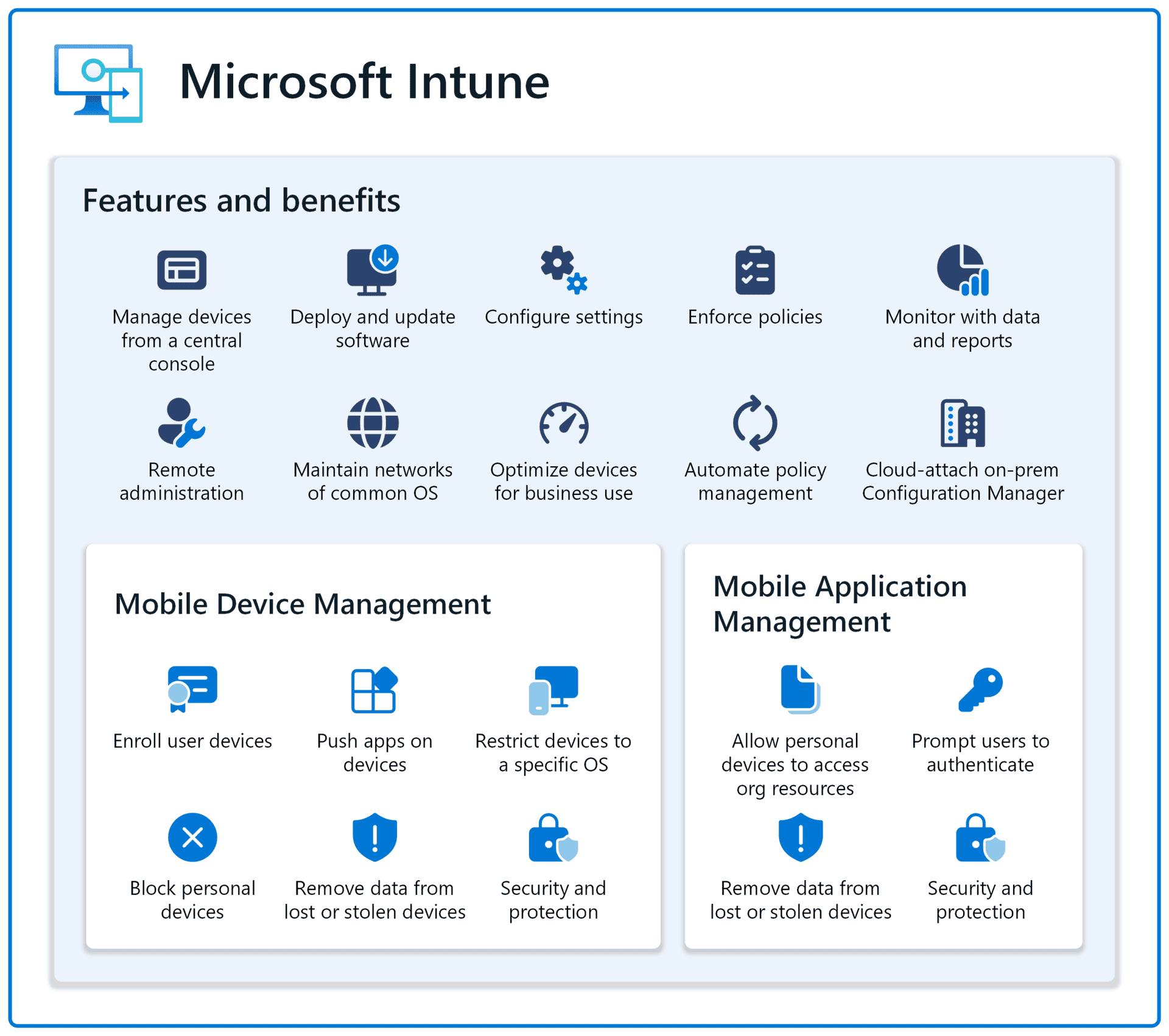
Microsoft Intune
Intune is a cloud-based MDM solution that enables organizations to manage a wide range of devices, including iOS, Android, Windows, and macOS. It provides a centralized platform for managing device settings, apps, and security policies.
Key Features:
- Device Enrollment: Easily enroll devices in Intune, whether they are corporate-owned or employee-owned (BYOD).
- App Management: Distribute, manage, and protect mobile apps, including both in-house and third-party apps.
- Compliance Policies: Enforce security policies, such as password requirements, encryption, and device restrictions.
- Conditional Access: Control access to corporate resources based on device compliance and user identity.
- Remote Actions: Perform remote actions on devices, such as lock, wipe, and locate.
Microsoft Endpoint Manager
Endpoint Manager is a unified platform that combines Intune with Configuration Manager. It provides a comprehensive solution for managing all endpoints, including desktops, laptops, and mobile devices.
Key Benefits:
- Unified Management: Manage all your devices from a single console.
- Enhanced Security: Protect your organization from cyber threats with advanced security features.
- Streamlined Compliance: Ensure compliance with industry regulations and corporate policies.
- Improved Productivity: Empower employees to work from anywhere with secure access to corporate resources.
Choosing the Right Solution
The best Microsoft MDM solution for your organization will depend on your specific needs and requirements.
- Intune: A good choice for organizations that primarily need to manage mobile devices and have a cloud-first strategy.
- Endpoint Manager: A more comprehensive solution that is suitable for organizations that need to manage all their endpoints, including desktops, laptops, and servers.
Considerations
- Device Types: The types of devices you need to manage (iOS, Android, Windows, macOS).
- Management Needs: The level of control you need over devices (device settings, app management, security policies).
- Deployment Model: Cloud-only, on-premises, or hybrid.
- Integration: Integration with other Microsoft services, such as Azure Active Directory and Microsoft 365.
Best Practices
- Plan Your Deployment: Define your MDM goals and objectives before you start.
- Enforce Strong Security Policies: Implement strong password policies, encryption, and other security measures.
- Educate Your Users: Train your employees on how to use their devices securely and comply with corporate policies.
- Monitor and Maintain: Regularly monitor your MDM solution and make adjustments as needed.
By implementing a Microsoft MDM solution, you can effectively manage and secure your mobile devices, protect corporate data, and improve employee productivity.
Security Considerations for Mobile Devices
Mobile devices have become essential tools for businesses, but they also pose significant security risks. Here are some key security considerations for mobile devices:
- Data Loss Prevention: Implement measures to prevent sensitive data from being lost or stolen, such as encryption, remote wipe, and data loss prevention (DLP) solutions.
- Malware Protection: Protect devices from malware and other threats with mobile threat defense (MTD) solutions.
- Secure Access: Control access to corporate resources with strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- App Security: Ensure that only authorized apps are installed on devices and that apps are kept up to date.
- Network Security: Use virtual private networks (VPNs) to secure connections to corporate networks.
- Device Management: Implement a mobile device management (MDM) solution to manage and secure devices.
By addressing these security considerations, you can help to protect your organization from the risks associated with mobile devices.
Key Takeaways
- Microsoft MDM enables secure management of company and personal devices
- Intune provides cloud-based tools for device enrollment and policy enforcement
- MDM solutions balance organizational security with user privacy concerns
Overview of Microsoft Mobile Device Management
Microsoft’s mobile device management solutions have evolved to meet the changing needs of modern enterprises. These tools provide comprehensive control and security for diverse device ecosystems.
Evolution of Device Management
Microsoft’s device management journey began with on-premises solutions and has transitioned to cloud-based platforms. The company’s early offerings focused on basic device control. Today, Microsoft 365 and Intune provide advanced features for managing mobile devices, PCs, and apps.
These solutions now support a wide range of operating systems. They offer capabilities like remote wipe, policy enforcement, and app management. Microsoft has also integrated artificial intelligence to enhance security and streamline management tasks.
Recent updates have improved support for BYOD scenarios. This allows organizations to secure corporate data on personal devices without compromising user privacy.
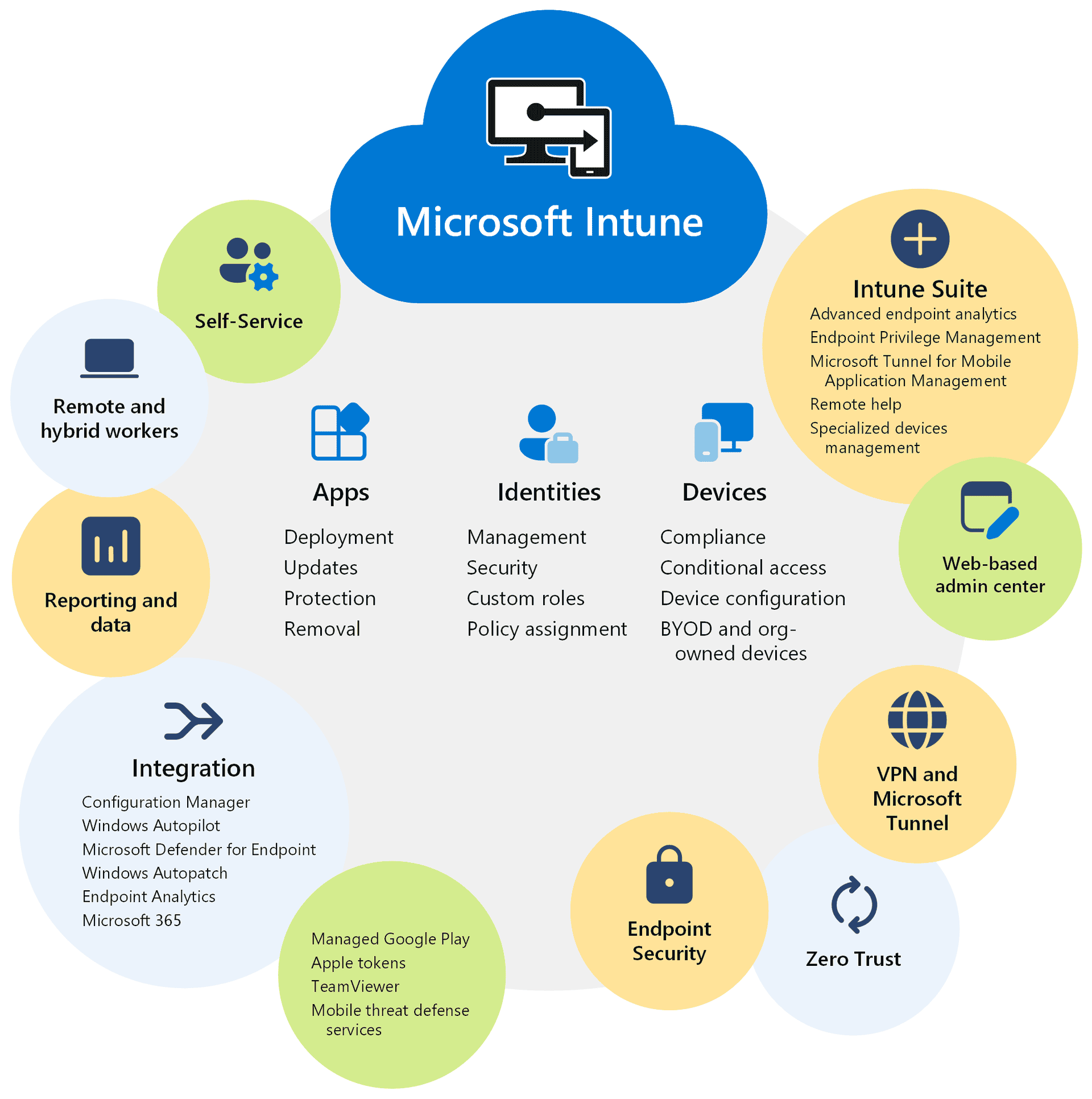
Microsoft’s Ecosystem for MDM
Microsoft’s mobile device management ecosystem centers around Microsoft Intune. This cloud-based service integrates with other Microsoft 365 components for comprehensive endpoint management.
Key features of Microsoft’s MDM ecosystem include:
- Device enrollment and configuration
- App deployment and management
- Data protection and compliance enforcement
- Threat detection and response
Intune works alongside Azure Active Directory for identity management. It also integrates with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to provide advanced security capabilities.
For on-premises needs, Microsoft offers Configuration Manager. This tool can be used in conjunction with Intune for a hybrid management approach.
Microsoft continues to expand its MDM capabilities. Recent additions include improved support for non-Windows devices and enhanced automation features.
Setting Up Microsoft Intune
Microsoft Intune simplifies mobile device management. It offers tools for device enrollment, application management, and user group organization.
Device Enrollment Process
Intune’s device enrollment process starts with setting the mobile device management (MDM) authority. IT admins must choose Intune as the MDM authority before users can enroll devices. The enrollment steps vary by device type and operating system.
For Windows devices, users can enroll through settings or by joining Azure AD. iOS and Android devices typically use the Company Portal app. Admins can also use Apple’s Device Enrollment Program for iOS devices or Android Enterprise for Android devices.
Bulk enrollment options exist for large-scale deployments. These include using provisioning packages or hardware IDs for Windows devices.
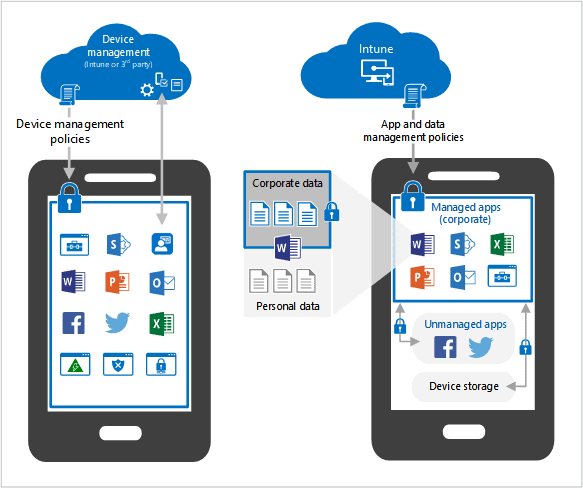
Mobile Application Management Overview
Intune’s Mobile Application Management (MAM) protects company data in mobile apps. It works on both enrolled and unenrolled devices.
Key MAM features:
- App protection policies
- App configuration policies
- App-based conditional access
Admins add or configure apps in the Intune admin center. These apps become “managed” by Intune when installed on devices. App protection policies can then be applied to these managed apps.
MAM without enrollment (MAM-WE) allows data protection on personal devices without full device management. This option suits bring-your-own-device (BYOD) scenarios.
User and Device Groups
Intune uses Azure AD groups to organize users and devices. These groups help target policies and apps to specific sets of users or devices.
Common group types:
- Dynamic groups (based on attributes)
- Assigned groups (manually managed)
Security groups often align with organizational structures like departments or job roles. Device groups may be based on device type, operating system, or ownership status.
Best practices include creating a hierarchy of groups and using naming conventions. This structure allows for granular policy application and easier management of large device fleets.
Security and Compliance
Microsoft’s mobile device management solutions prioritize robust security measures and compliance tools. These features protect company data, enforce policies, and enable remote device control.
Creating and Managing Device Security Policies
Device security policies form the backbone of mobile device management. Administrators can create and apply policies to groups of users through Basic Mobility and Security. These policies control settings like password requirements, encryption, and app restrictions.
To set up policies:
- Access the Security & Compliance Center
- Navigate to Data loss prevention > Device management
- Create new policies or edit existing ones
- Assign policies to user groups
Policies can enforce various security measures:
- Minimum password length and complexity
- Device encryption
- Blocked apps list
- Camera usage restrictions
- Cloud backup controls
Regular policy reviews ensure optimal protection as threats evolve.
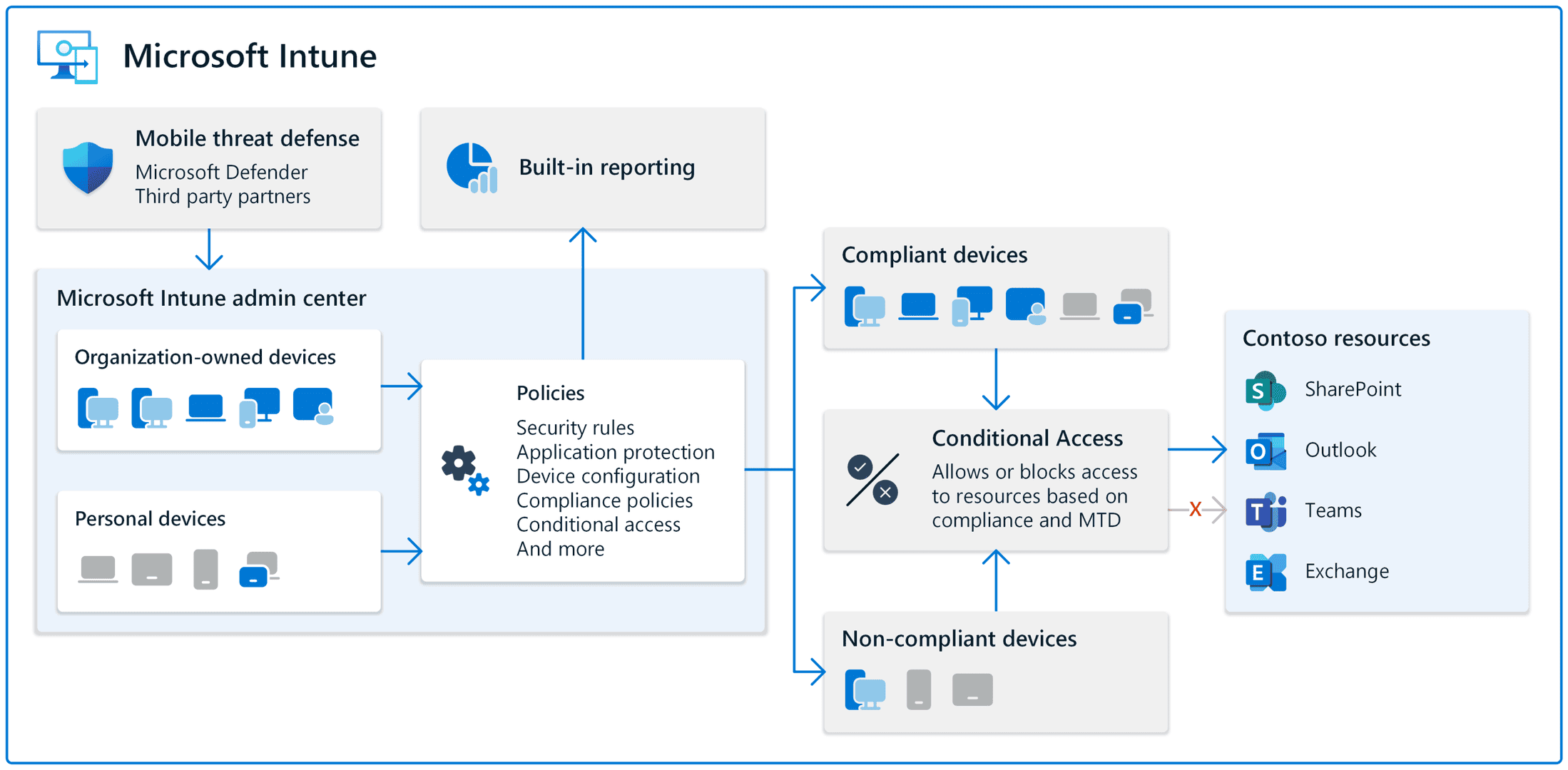
Compliance Policies and Conditional Access
Compliance policies work alongside security policies to maintain data protection standards. These policies define rules devices must meet to access company resources.
Key compliance features include:
- Device health checks
- Operating system version requirements
- Jailbreak/root detection
- Malware scans
Conditional Access enhances security by controlling resource access based on user, device, and risk factors. It integrates with Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) for identity-based protection.
Administrators can set up rules like:
- Require multi-factor authentication for sensitive apps
- Block access from untrusted locations
- Limit access to specific device types or OS versions
This granular control helps prevent unauthorized data access.
Remotely Managing Company Devices
Remote management capabilities give IT teams powerful tools to protect company data on mobile devices. These features are crucial for addressing security incidents and managing lost or stolen devices.
Key remote management actions:
- Full or selective device wipe
- Password reset
- Device lock
- App removal
- Data encryption enforcement
Administrators can perform these actions through the Microsoft 365 admin center or Intune portal. For urgent situations, like a lost device, quick action can prevent data breaches.
Remote management also enables:
- Software updates and patch management
- Configuration changes
- Inventory tracking
- Device diagnostics
These tools ensure devices remain secure and compliant, even when physically out of IT’s reach.
Application Deployment and Management
Microsoft’s mobile device management solutions offer powerful tools for deploying and managing applications across devices. These capabilities streamline app distribution, ensure security, and enable efficient management of business applications.
App Deployment with Microsoft Intune
Microsoft Intune simplifies app deployment to mobile devices. IT administrators can push apps to devices or make them available for users to install through the Company Portal app.
Intune supports various app types, including:
- Store apps (iOS App Store, Google Play)
- Line-of-business apps
- Web apps
The platform allows admins to assign apps to specific users or groups. This targeting ensures employees have access to the right tools for their roles.
Intune also enables app configuration during deployment. Admins can pre-configure app settings, reducing setup time for users and ensuring consistent configurations across devices.
Managing Business Applications
Effective management of business applications is crucial for productivity and security. Microsoft’s mobile application management (MAM) features provide granular control over app behavior and data access.
Key MAM capabilities include:
- Data protection policies
- App-level VPN
- App update management
- Usage reporting
Admins can apply these controls to both company-owned and personal devices. This flexibility supports bring-your-own-device (BYOD) scenarios while maintaining data security.
MAM policies can restrict actions like copy-paste between apps or prevent saving to personal cloud storage. These measures help prevent data leaks and maintain compliance with organizational policies.
Use Case: Microsoft Edge Management
Microsoft Edge serves as an example of comprehensive app management. IT teams can deploy and configure Edge across mobile devices using Intune.
Key management features for Edge include:
- Enforcing security settings
- Configuring default homepage and favorites
- Managing browser extensions
Admins can push policies that require authentication for accessing company resources through Edge. This ensures only authorized users can access sensitive data.
Edge management also allows for content filtering and safe browsing policies. These features protect users from malicious websites and help maintain productivity by limiting access to non-work-related content.
Frequently Asked Questions
Microsoft’s Mobile Device Management (MDM) offers a range of features for various devices and operating systems. Users often have questions about its capabilities, settings, and privacy implications.
How does Microsoft’s Mobile Device Management handle Android devices?
Microsoft MDM supports Android devices through its management protocols. It allows IT administrators to enforce security policies, manage apps, and configure device settings remotely. Android devices can be enrolled in MDM using the Company Portal app or through other approved methods.
What features can I find in Mobile Device Management for Windows 11?
MDM for Windows 11 includes enhanced security features and management options. It supports remote device wipe, app installation control, and advanced network configurations. Windows 11 devices can be managed more granularly, with options for firmware and driver updates through MDM.
Where can I access the settings for Microsoft’s Mobile Device Management?
MDM settings are typically accessed through the Microsoft 365 admin center or the Azure portal. IT administrators can configure policies, view device status, and manage enrolled devices from these central management consoles.
Can I download a standalone application for Microsoft MDM?
Microsoft does not offer a standalone MDM application. Instead, MDM functionality is integrated into existing Microsoft services and platforms. Users interact with MDM through built-in device features or the Company Portal app on mobile devices.
How does Microsoft MDM compare to Intune in terms of features and capabilities?
Microsoft Intune is actually the core component of Microsoft’s MDM solution. It offers more advanced features compared to basic MDM, including app protection policies and conditional access. Intune provides a comprehensive suite of mobile device and application management tools.
What privacy concerns should I be aware of when using Microsoft’s MDM on my device?
MDM can access certain device information and enforce policies. Users should be aware that IT administrators may have the ability to view device location, installed apps, and usage data. Personal data is generally not accessible, but company data can be remotely wiped if necessary.